Matter: The Future of Smart Home Connectivity and Its Impact on Product Development
Understanding Matter's role in standardizing smart home communication, endorsed by industry leaders and aimed at transforming IoT product development by addressing device compatibility issues.

Introduction
The advent of the Matter protocol marks a significant milestone in the evolution of smart home connectivity. Matter, an open-source, royalty-free connectivity standard, is poised to revolutionize the Internet of Things (IoT) landscape by providing a unified protocol for smart home devices1. This protocol, built on Internet Protocol (IP) technology, simplifies and standardizes communication among smart devices, fostering a more cohesive and user-friendly smart home ecosystem5.
The endorsement of Matter by tech giants Amazon, Google, and Apple underscores its potential to become the de facto standard for smart home connectivity2. Their agreement on Matter is a testament to the protocol's robustness and ability to address the long-standing issue of device interoperability. This consensus among industry leaders is expected to accelerate the adoption of Matter, thereby catalyzing the growth of the smart home market3.
With an increasing number of smart devices entering the market, the need for a common communication standard has led to a fragmented ecosystem where device compatibility is a constant challenge6. Matter aims to address this issue by providing a universal standard that ensures seamless device interaction, regardless of the manufacturer7. This enhances the user experience and simplifies the product development process, thus paving the way for the rapid proliferation of smart home devices8.
Engineers and developers are at a transformative phase in IoT product development as they navigate the opportunities and challenges Matter presents. This article explores the potential of Matter as a unifying force in the smart home ecosystem, its impact on IoT product development and integration, and what it means for the future of smart home connectivity.
Understanding the Matter Protocol
The Genesis of Matter
The Matter protocol represents a collaborative effort by major tech companies, including Amazon, Apple, Google, and the Zigbee Alliance, now known as the Connectivity Standards Alliance (CSA). Initiated in December 2019 under the Project Connected Home over IP (CHIP), the Matter standard aims to improve the compatibility and security of smart home and Internet of Things (IoT) devices.
The protocol became official in November 2022, and software updates for many existing devices were made available by the end of the same year, with additional Matter-enabled devices and software updates expected to roll out throughout 2023.
The Connectivity Standards Alliance and its mission
The CSA, formerly the Zigbee Alliance, maintains the Matter standard. The alliance encourages interoperability between devices and platforms and aims to simplify development for innovative home product brands and manufacturers.
Adopting a universal standard such as Matter addresses the issues of device incompatibility and reliance on proprietary hubs, often associated with IoT devices. The Matter is an IP-based standard that allows products to run locally without an internet connection while still being able to connect to the cloud. This design increases the compatibility and security of the products, making it an effective solution to the challenges that have long plagued the smart home industry.
The Functionality of Matter
How Matter Works
Matter is an open-source connectivity standard for smart home and Internet of Things (IoT) devices, aiming to improve their compatibility and security. Based on Internet Protocol (IP), Matter functions through compatible border routers, reducing the need for multiple proprietary hubs. Products operating under the Matter standard can run locally without an internet connection but are designed to connect to the cloud easily.
The Matter standard enables cross-platform operation of smart home devices, mobile apps, and cloud services. Importantly, Matter devices continue to function together even without an internet connection due to the integration of Thread. This low-powered mesh-based wireless protocol creates a low-latency offline environment for data transmission.
Architecture of Matter
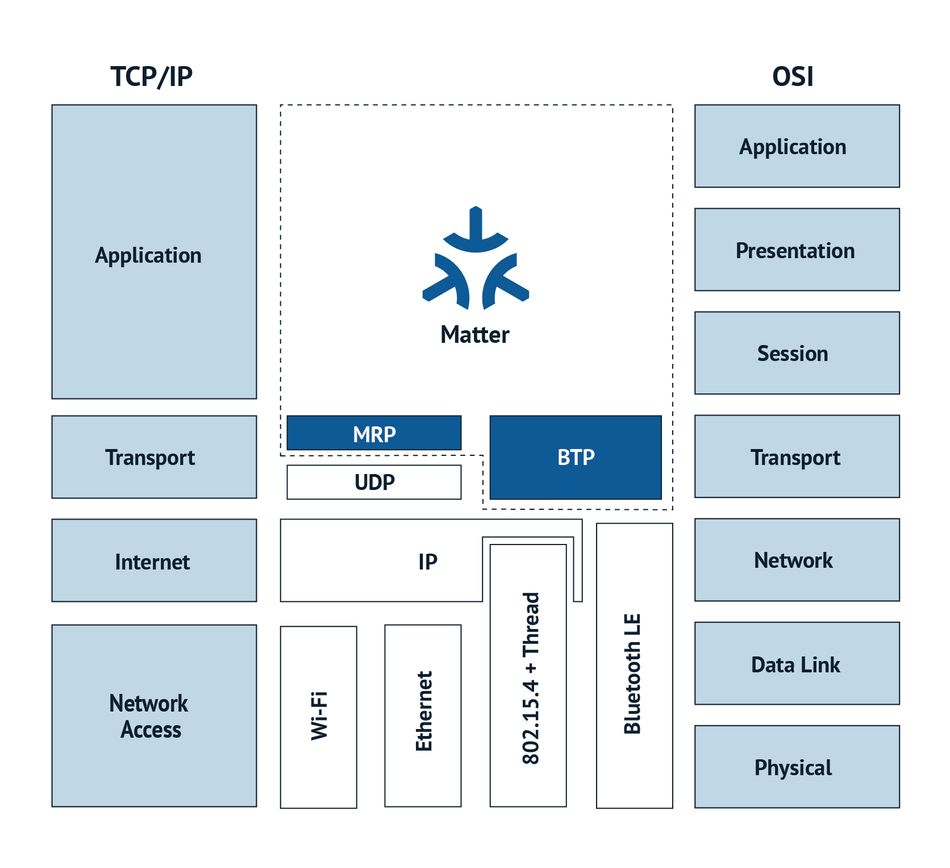
The Matter protocol, designed to establish a universal IPv6-based communication standard for smart home devices, is structured into distinct layers to encapsulate various responsibilities and components of the protocol stack. Figure 1
- The application layer, the highest layer, encapsulates the high-order business logic of a device. For instance, a lighting-focused application might contain logic to manage the bulbs on/off state and color characteristics.
- The data model layer, which supports the application's functionality, corresponds to the data and verb elements that the application operates on when interacting with the device.
- The interaction model layer defines a set of interactions that can be performed between a client and server device. These interactions, which operate on the elements defined at the data model layer, are serialized into a prescribed packed binary format for network transmission once an action is constructed using the interaction model.
- This encoded action frame is then sent to the security layer to encrypt and sign the payload, ensuring data security and authentication by the sender and receiver of a packet.
- The message layer constructs the payload format with required and optional header fields, specifying the message's properties and some routing information. After the final payload has been constructed, it is sent to the underlying transport protocol for IP management of the data14.
The Benefits of a Unified Protocol
Matter's IP-based networking technology simplifies the development of smart home product brands and manufacturers by providing a universal standard for device certification. This IP connectivity eliminates the need for multiple proprietary apps for different device brands, relieving the user from the stress of managing separate platforms for each smart home device. IP use also permits offline operation, overcoming one of the major pain points with existing IoT devices that require a continuous internet connection. Figure 2
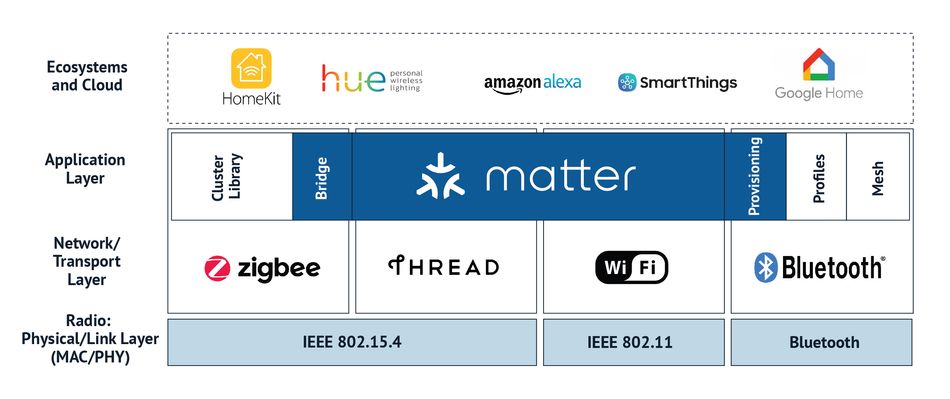
Matter's Impact on Smart Home Ecosystems
Interoperability of Devices
Matter's universal standard promotes interoperability between various devices and platforms. Key players like Google, Apple, and Amazon have added Matter support to their devices, with other companies expected to follow suit. This broad adoption means users can control Matter-enabled smart devices across different ecosystems, regardless of the original setup device. The increasing number of Matter-enabled devices from other brands further enhances this interoperability.
Enhanced Security and Privacy
The ability for Matter devices to work offline reduces their reliance on the cloud, thereby improving security, particularly for sensitive hardware like smart locks and security cameras. This feature is a significant advantage of Matter over traditional IoT devices that rely heavily on cloud services.
With the integration of Matter and the Thread wireless protocol, a future where Matter-certified products work together in synchronous harmony, even without an internet connection. This ability to achieve complete offline computing within a local mesh network of IoT devices marks a significant step forward in the evolution of smart homes. Figure 3
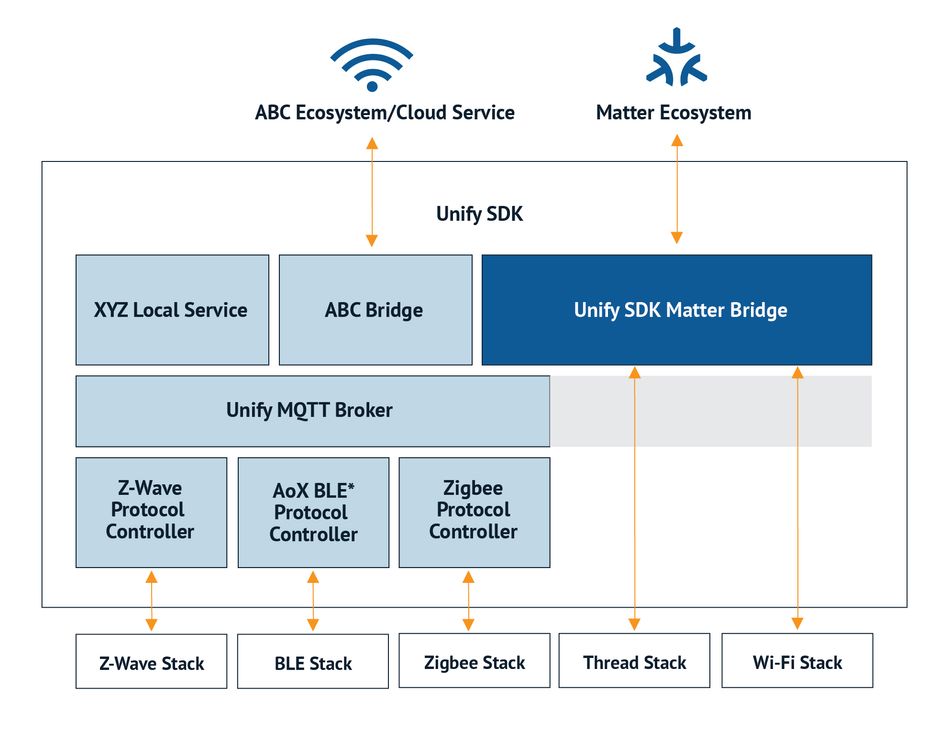
The Matter Software Development Kit (SDK)
The Matter SDK is an open-source toolkit that forms the backbone of the Matter protocol. It provides developers a structured approach to integrating the Matter standard into their IoT devices. The SDK, first made publicly available in October 2022, is built upon Internet Protocol (IP) technology and is designed to simplify the development process, thus accelerating the time to market for new products.
An Overview of the SDK
The SDK offers a comprehensive set of tools for developing Matter-compatible devices. It includes APIs for device certification and facilitates cross-platform integration of smart home devices, mobile apps, and cloud services. Moreover, the SDK also supports the Thread wireless protocol, which enables low-latency data transfer between devices in a local network.
The Matter SDK plays a crucial role in product development. It reduces the complexity of developing IoT devices and provides a standardized protocol for device communication. This results in a unified smart home ecosystem where devices from different manufacturers can interact seamlessly.
In 2023, Google and Apple incorporated Matter support into their devices. Google's Nest Hub, Nest Wifi, and Wifi Pro routers, along with Apple's iPhone, iPad, HomeKit, Apple TV 4K, and HomePod Mini, are all Matter-compatible. These devices can function as Matter controllers and Thread border routers, which is crucial for smart home ecosystems. Google uses Fast Pair for device addition, while Apple's Home app facilitates the integration of Matter devices.
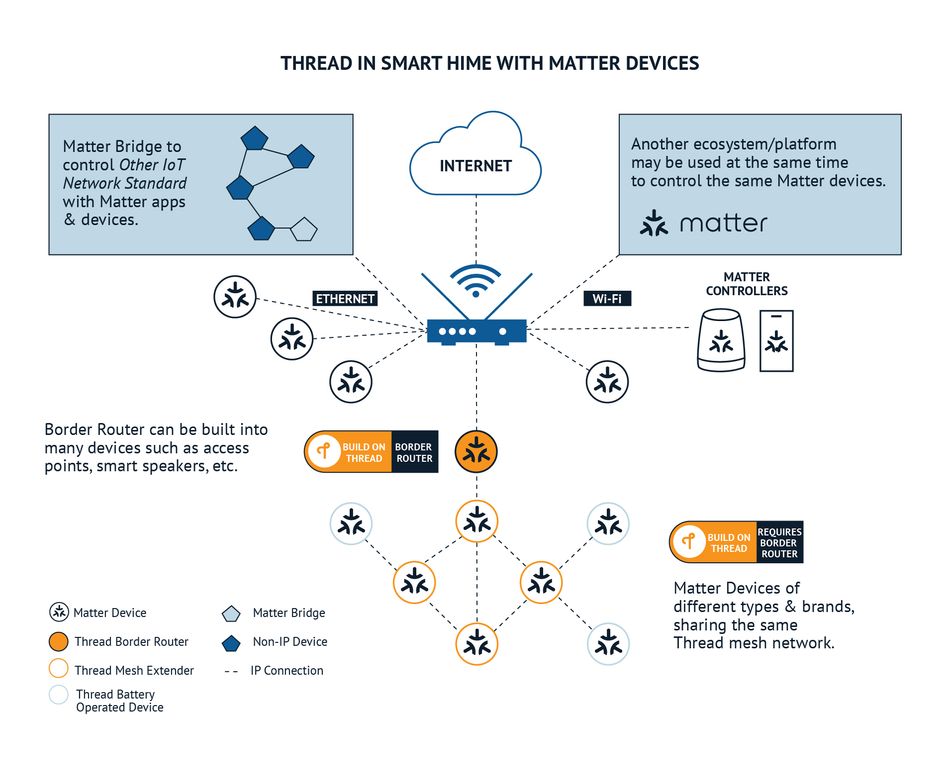
Integrating Matter into Existing Products
The integration of Matter into existing products entails software updates that are compatible with the Matter standard. These updates are designed to improve device interoperability and security. The Matter protocol runs locally, allowing devices to function without a constant internet connection, yet can communicate seamlessly with the cloud. Figure 4
Developers face the challenge of juggling across multiple proprietary apps. Matter addresses this by enabling cross-platform integration, simplifying the developer's task. Additionally, Thread, a low-latency offline protocol, complements Matter, allowing devices to interact even without an internet connection.
Future Prospects with Matter
Matter, a royalty-free standard, is poised to revolutionize the IoT market with its cost efficiency, standardization, and security. As tech giants like Google, Apple, and Amazon integrate Matter into their products, we anticipate a surge in Matter-compliant devices in 2023. Including the Thread wireless protocol could create an offline local mesh network of IoT devices, transforming smart home technology.
The Matter standard is also expected to simplify smart home ecosystems, allowing devices from different manufacturers to work harmoniously. Furthermore, the adoption of Matter by major smart home brands like August, Schlage, and Yale, and the support from over 280 member companies, indicates a promising future for this standard. We predict a significant increase in Matter-enabled smart devices as Matter development progresses, potentially reshaping the IoT landscape6.
Conclusion
Matter offers a promising future for the development of IoT products. Its focus on standardization, security, and interoperability paves the way for a more cohesive and efficient smart home environment. However, like any emerging technology, it will require continuous refinement and adaptation to meet the evolving needs of users and developers.
Listen to more about Matter with Mouser
Smart home ecosystems are ready for an interpreter. Listen in to The Tech Between Us as Raymond Yin, Director of Technical Content at Mouser speaks with Chris LaPré, Chief Technical Officer at the Connectivity Standards Alliance as they discuss the significance of Matter’s introduction to the market.
References
[1] Matter: The Future of Reliable Connectivity
[2] Matter: The Connectivity Standard for the Future of the Smart Home
[3] Matter: The New Smart Home Standard
[4] Matter: The Open-Source, Royalty-Free Connectivity Standard
[5] Matter: The Unified IP-Based Connectivity Protocol
[6] Matter: The Future of Smart Home Devices
[7] Matter: The New Connectivity Standard
[8] Matter: The Standard for Connected Things
[9] Matter: The Universal Smart Home Standard
[10]Matter: The Standard for Future IoT Devices
[11]Connectivity Standards Alliance. (2023). Introduction to Matter. CSA.
[12]Matter. (2023). Technical Overview. Matter.
[13]LaPré, C. (2023). Tech Giants Agree on Matter. Mouser Electronics.
