Types of 3D Printers and Printing Techniques: A quick overview
Understanding the different types of 3D printers available in the market will help ensure that you select the best product for your operations.

Plastic is ubiquitous in our modern world, a staple of many manufacturing components and consumer products. With its versatility and low cost, it is suitable for a wide range of purposes. But along with plastic’s versatility, comes the need to decide between the various alternatives for its design, manufacture and assembly.
3D printing is an additive manufacturing technology that creates a plastic print by iteratively layering the requisite materials onto one another until the final product is complete. 3D printing is usually faster than conventional alternatives for plastic fabrication, which has made it an increasingly popular choice for modern businesses.
How many types of 3D printers are there?
Several different additive manufacturing techniques are employed in modern 3D printing. Depending on your timeline, budget, and product requirements, some 3D printing techniques and types of 3D printers will fit your project better than others. Here we examine the different techniques, along with their relative advantages, disadvantages, and most common use cases.
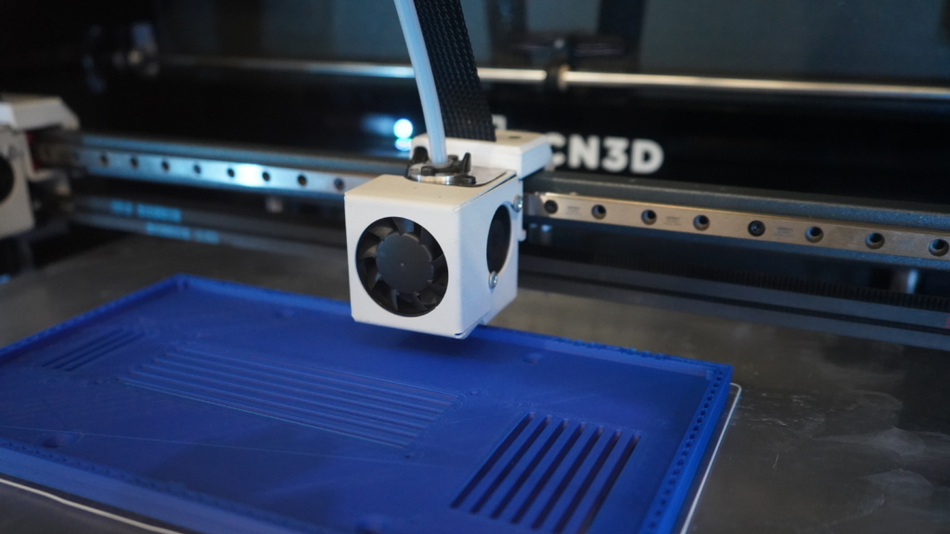
1. Extrusion – FFF
Extrusion – FFF creates objects by depositing layers of melted thermoplastic polymers. It is most commonly used for constructing visual aids and prototypes. A broad variety of compatible materials can be used to fulfill all requirements. This technique can produce functional parts for a wide range of applications.
Advantages:
- Fast printing speed
- Ability to create end-use parts
- Large range of compatible materials
Disadvantages:
- Visible layer lines
- Less detail than other methods
2. Vat Polymerization – SLA
Vat Polymerization – SLA uses UV laser light to selectively photo-polymerize a vat of liquid curable resin, creating a solid model. It is a highly accurate technique that produces a good surface finish. It is mainly used for the creation of visual aids and prototypes, as well as casting moulds.
Advantages:
- Highly accurate
- Very precise
- Smooth surface quality
Disadvantages:
- Parts tend to degrade in sunlight
- Low mechanical properties
- Requires mechanical support removal
3. Vat Polymerization – DLP
Vat Polymerization – DLP also selectively photo-polymerizes a vat of liquid curable resin to create a solid model. While similar to SLA in its use of curable resin, the two techniques differ in the type of light source used to cure the photopolymer. DLP uses light from a digital light projector screen, and creates only a single image per layer. Its high precision makes it a popular choice for casting moulds and creating visual aids and prototypes.
Advantages:
- Highly accurate
- Very precise
- Smooth surface quality
Disadvantages:
- Parts tend to degrade in sunlight
- Offers low mechanical properties
- Requires mechanical support removal

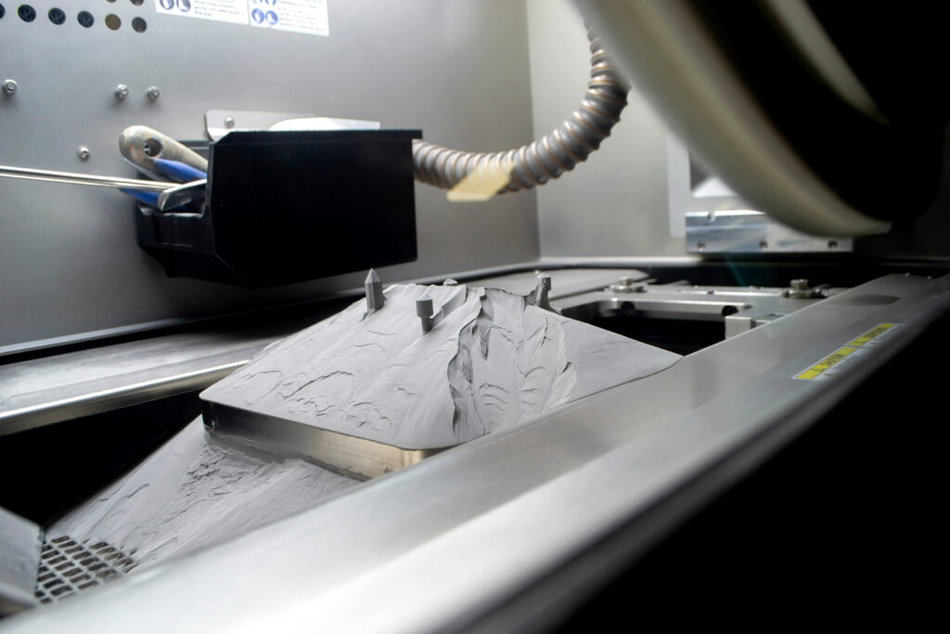
4. Powder Bed Fusion
Powder Bed Fusion uses high powered lasers to selectively sinter powdered plastic materials. It is most commonly used for prototyping, functional testing, and the creation of manufacturing aids. It is also very popular for small-series part production.
Advantages:
- Ideal for complex geometries
- Good for small-series part production
Disadvantages:
- Higher cost than most other techniques
- Grainy and porous surface result
5. Material Jetting
Material Jetting deposits and cures material droplets using photopolymers sensitive to UV light. It is most often used for prototyping and casting moulds.
Advantages:
- Enables full-color prototyping
- Excellent surface quality
- Highly accurate
- Good level of detail
Disadvantages:
- Offers low material properties
- Works with a limited range of materials
6. Binder Jetting
Binder Jetting uses a liquid bonding material to bind parts of a powder bed together. It is mainly used for full-color prototyping and pattern casting.
Advantages:
- Enables full-color model production
- Good surface quality
Disadvantages:
- Offers limited mechanical properties
- Parts tend to be fragile and brittle
Types of 3D Printers: Choosing the right one for your project
Additive manufacturing technologies are excellent for producing a modest quantity of parts at low cost and with short lead times. The various types of 3D printers are also ideal for creating parts with complex geometries at a level of precision that cannot be replicated by alternate fabrication methods.
While a wide variety of technologies are now available for plastic part fabrication, some methods will be more fitting than others for any particular application. The requirements for the final product, the volume of parts needed, and the available budget will largely dictate the chosen technology. The properties of the plastic will also determine which manufacturing methods and processing parameters will be feasible. Should you still be craving more information, download our white paper for a walkthrough of the 3D printing process or have a one-on-one chat with one of our 3D printing experts by booking a demo below!