A quick engineering comparison of cutting-edge humanoid robots
Exploring innovations, capabilities, and the future of robotic companions
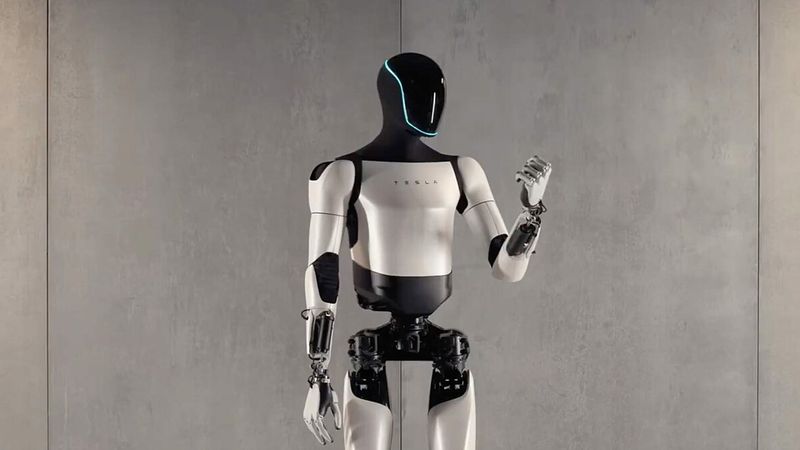

Image credit: Tesla via Wiki Commons
Humanoid robots are designed to resemble and mimic human actions and interactions, placing them as a bridge forming collaborations between humans and machines. Their human-like appearance and movements create a sense of relatability and approachability not typically seen in traditional industrial robots. This "personal appeal" has sparked increased interest in developing humanoid robots for diverse applications, such as healthcare, customer service, education, and even space exploration - where human characteristics such as empathy, decision-making making, and personality are deemed valuable.
This article provides insights into four of the leading humanoid robot projects from around the world.
Selection Rationale
The humanoid robots selected in this comparison represent the pinnacle of the current state of humanoid robotic technology. Each robot was selected based on its unique contributions to its field, ranging from technical capabilities to broadest application.
Each selected robot is also in full production and either available for purchase or being used by their creators in real-time applications.
Optimus by Tesla
Also known as Tesla Bot, this general-purpose, bipedal, autonomous humanoid robot was created to perform unsafe, repetitive, or boring tasks. The company announced the robot's development in August 2021 and showed the prototype in 2022. Tesla's CEO, Elon Musk, claimed that Optimus will eventually be able to do "anything that humans don’t want to do."
Tesla's Optimus can sort colored blocks by color, locate its limbs in space, do some yoga, and even poach an egg. In December 2023, Musk released a video showing an Optimus Generation 2 walking and dancing. The new robot features a slimmer figure and sleeker, more precise movements.
The robot is planned to measure 5 ft 8 in (173 cm) tall and weigh 125 lb (57 kg), and it will be controlled by the same AI system that Tesla uses in its cars. With a carrying capacity of 45 lb (20 kg), it can provide manufacturing assistance, and Musk has already commented that the robots will be utilized in Tesla’s car factories by the end of 2024 to enhance the factory's efficiency and significantly reduce production costs.
The first commercial units of Tesla's Optimus will launch in 2025.
Atlas by Boston Dynamics
Atlas, engineered by leading robotic company Boston Dynamics, represents a huge leap forward for robotic mobility and adaptability. Debuting on July 11, 2013, Atlas was designed to traverse and interact with its surroundings with a fluidity and precision reminiscent of human motion. Constructed with robust plastics, titanium, and aluminum 3D printed parts, Atlas was originally driven by powerful hydraulic actuators, but now, the company has announced a fully electric robot. In widely shared videos, Atlas has demonstrated a broad spectrum of physical prowess, including running, leaping, and executing backflips easily. These types of motion are difficult as they require the robot to self-correct and consider environmental factors.
Atlas uses a comprehensive sensor network powered by AI to facilitate meticulous navigation and the proficient completion of multifaceted tasks across diverse landscapes. Such capabilities mean Atlas may have a future in scenarios such as search and rescue or fire management, where its agility and adaptability can be leveraged to great effect.
After being acquired by Hyundai in 2021, the focus will be testing and iterating Atlas applications in manufacturing environments. The company promises that the electric version of Atlas is stronger and has a broader range of motion than previous models.
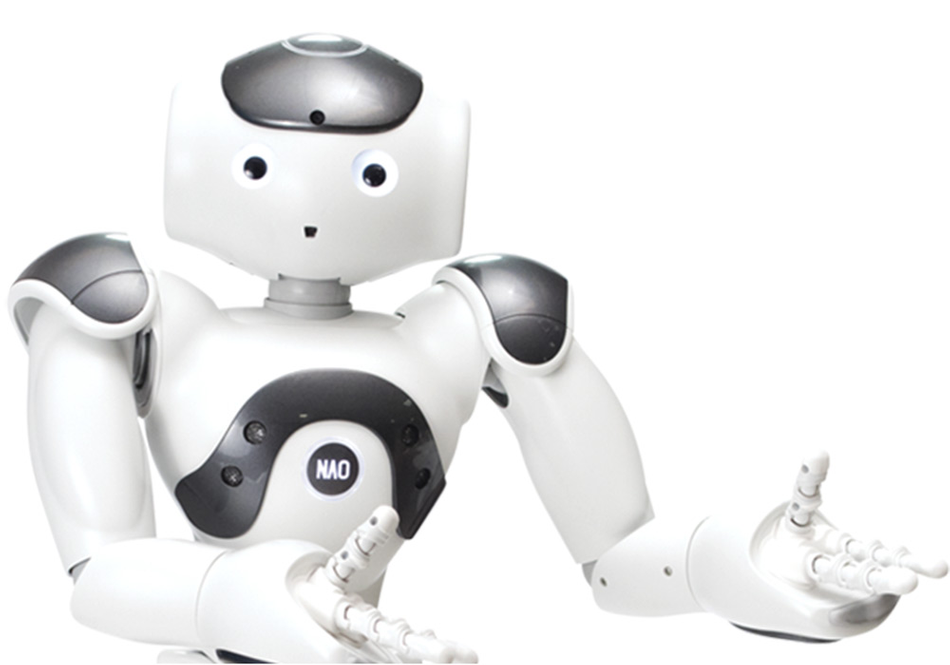
NAO by Aldebaran
NAO is an autonomous, programmable humanoid robot originally developed by Aldebaran Robotics. SoftBank Robotics acquired the French company in 2015 and released NAO 3. In July 2022, the company was rebranded Aldebaran again.
Nao is available as a research robot for schools, colleges and universities to teach programming as well as conducting research into human-robot interactions. Over 5,000 Nao robots are used in 200+ educational and research institutions in 70 countries. The robots are also used in healthcare scenarios, such as care homes.
NAO6, the latest version, features 25 degrees of freedom and an inertial measurement unit with an accelerometer, gyroscope, and four ultrasonic sensors that support NAO with stability and movement. The robots are also equipped with seven touch sensors to perceive their environment and their speech recognition is available in 20 languages. The robot also has 5G capabilities.
Ameca by Engineered Arts
Ameca, first developed by Engineered Arts in February 2021, is currently the most advanced human-shaped robot in the market, developed specifically for human-robot interaction. They are modular, upgradable, and easy to develop upon.
With embedded microphones, binocular eye-mounted cameras, a chest camera, and facial recognition software, Ameca's interactions with the public work by GPT-3 or human telepresence. It also has motorized arms, fingers, neck, and facial features on grey rubber skin, designed to appear genderless. Engineered Arts has developed their own hardware, based on proprietory research into humanoid robotics, and built with their Mesmer technology, a system focused on powerful, cost-effective, and realistic humanoid robots.
Ameca is currently associated with the Museum of the Future in Dubai (UEA), where people can interact with it.
Technology Overview
Robot | Company/ Creator | Vision & Goal | Materials | AI Capabilities & Technology | Applications | Command & Agility |
Optimus | Tesla | Replace humans in manufacturing operations for repetitive and dangerous tasks | Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK) | Tesla-designed actuators and sensors | Manufacturing support and training | Carrying capacity of 20kg, can dance, boil eggs, do squats |
Atlas | Boston Dynamics | Navigate and manipulate environments with human-like agility | Titanium and aluminum | Precise navigation, execution of complex tasks in varied terrains | Search and rescue, exploration, logistics | Responsive to commands, capable of running, jumping, performing backflips |
NAO | Aldebaran | Human interaction and educational support | Polycarbonate-ABS plastic, polyamide, and carbon-fiber-reinforced thermoplastic | Conversational AI, personalized interaction based on facial recognition, collect information | Education, research, healthcare | Walk, dance, speak, and recognize faces and objects |
Ameca | Engineered Arts | Development platform for testing AI and machine learning systems | Mesmer technology | Process complex data, recognize faces, comprehend speech, and adapt to different scenarios | Human interaction, a platform for developing AI | Advanced facial expression and human-like interactions |
Conclusion: The Pioneers of Humanoid Robotics - A Unified Perspective
The exploration of Optimus, Atlas, NAO, and Ameca highlights the remarkable journey and achievements in humanoid robotics. Each robot, distinct in its capabilities and applications, contributes uniquely to the field. From Ameca's social interactions to Atlas's agility, NAO's educational support, and Optimus's manufacturing utility, these pioneers embody the diverse potential of robotics.
Their materiality and design philosophies are tailored to specific applications, showcasing innovation in construction and functionality. The AI and technological advancements across these robots cover a broad spectrum, enabling them to perform tasks ranging from basic interactions to complex, autonomous problem-solving. Their deployment in healthcare, customer service, manufacturing exploration, and emergency response illustrates the expanding role of robotics in meeting intricate human needs.
The integration of sophisticated command systems and remarkable agility demonstrates the evolving interface between humans and machines, pushing the boundaries of what humanoid robots can achieve. This unified perspective underlines the transformative impact of humanoid robotics, promising a future where their presence becomes an integral part of daily life and complex problem-solving across various sectors.