Design Guidelines for Manufacturing and Assembly
DFMA stands for Design for Manufacturing and Assembly. DFMA is designed to ensure product design at lower cost, shorter time and higher quality by improving product manufacturability and assemblability on the premise of taking product functionality, appearance and reliability into consideration.

Photo by Florian Klauer on Unsplash
Part I What’s the Concept of DFMA?
1. Manufacturability
Manufacturability refers to the ability of a part to be manufactured at a lower cost and higher quality. If the manufacturability of a part is high, then it means that the part meets the design requirements of the manufacturing process, it is easy to manufacture, its manufacturing efficiency is high, its cost is low, its defects are few, and its quality is high, etc.; Correspondingly, if the manufacturability of a part is low, the part does not meet the design requirements of the manufacturing process, it is difficult to manufacture, the efficiency is low, the cost is high, the many defects exist and the quality is low.
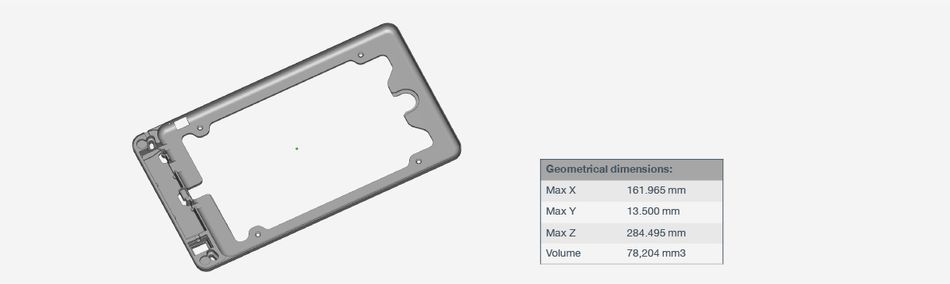
For example, plastic parts are manufactured by injection molding, then the design must meet the design of parts for injection processing. The manufacturability of plastic parts includes:
• Uniform wall thickness
• Avoid sharp corners
• Suitable draft angle
• Design of stiffeners, support pillars and holes
• Improve the design of the appearance of plastic parts
• Design to reduce the cost of plastic parts
• Feasibility of Injection mold designs
2. Assemblability
Manufacturability refers to the ability of a part to be manufactured at a lower cost and higher quality. If the manufacturability of a part is high, then it means that the part meets the design requirements of the manufacturing process, it is easy to manufacture, its manufacturing efficiency is high, its cost is low, its defects are few, and its quality is high, etc.; Correspondingly, if the manufacturability of a part is low, the part does not meet the design requirements of the manufacturing process, it is difficult to manufacture, the efficiency is low, the cost is high, the many defects exist and the quality is low.
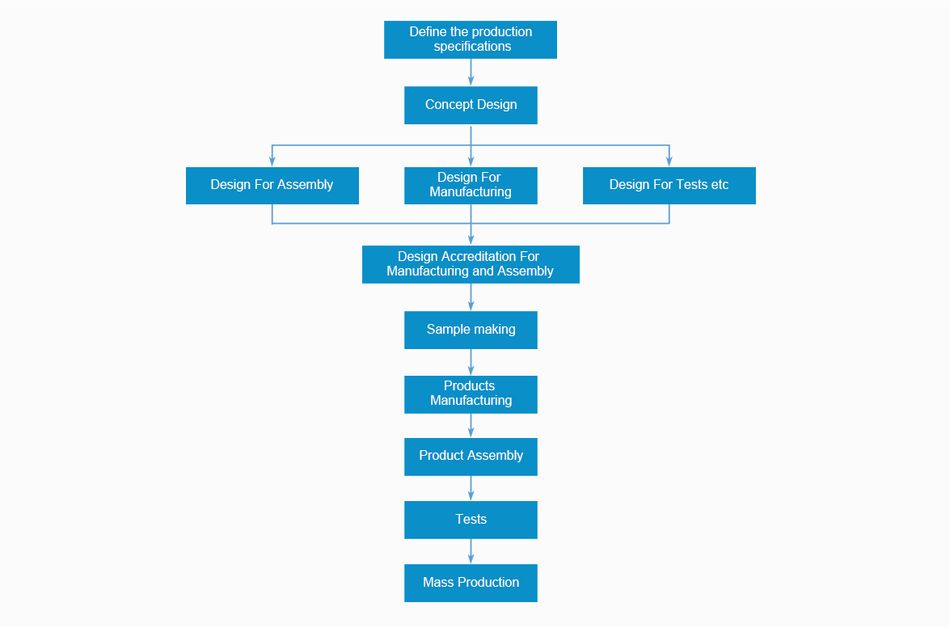
Part II What’s the Development Flow of DFMA
Part III What Are the Impediments for DFMA Implementation
1. Ignoring product design
Some companies pay no attention to product designs. They don’t think product design is important and are not willing to devote time and energy in product design.
2. Wrong product quality concept
Some companies believe that products are manufactured, and product quality is equal to manufacturing quality. This is the wrong product quality concept. Product quality is not manufactured, but designed.
3. No awareness for DFMA
Although many enterprises have paid attention to the manufacturability and assemblability of product design in the product design phase, however, they don’t consider the manufacturability and assemblability of product design systematically, so there is still a long way to go with real DFMA.
4. DFMA requires teamwork
DFMA requires a fundamental abandonment of long-term use of traditional product development processes, while the design department also needs to work in teams with manufacturing, assembly, testing, etc., which inevitably encounters many obstacles. DFMA requires not only product design engineers to consider the manufacturability and assemblability of the product, but also manufacturing and assembly engineers to offer ideas from their point of view. Therefore, DFMA requires teamwork and is not easy to implement.
5. Lack of DFMA talents
DFMA has high demand for product design engineers. They must be able to design based on various of design requirements and be familiar with manufacturing and assembly processes, which requires plenty accumulation of time and experience. There is a lack of talents in this area and companies also lack patience to train them.
6. Erroneous manufacturing positioning
Sometimes, the suppliers know that the product design is unreasonable so that the manufactured product cannot meet the design requirements, but in order to get the order, they accept the order without any design modification suggestions. In this case, product design often does not consider the requirements of manufacturing, which is wrong.
7. The misguidance from "customer first" principle
The “customer first” principle usually leads to neglect of product manufacturability and assemblability. When facing customers’ requirements, do not accept it directly, but consider product manufacturability and assemblability and analyze comprehensively with reasonable evidence, even if their requirements can’t be met, the customers will be impressed with the engineer’s professionalism and will not be unhappy with it, which can achieve a win-win situation between companies and their customers.