Smarter Security at the Edge: Reducing SWaP Demands with Neuromorphic AI
Discover how BrainChip’s Akida 1000, powered by neuromorphic AI, delivers real-time anomaly detection, ultra-low power consumption, and localized processing to protect critical industries.
In 2022, over 112 million IoT devices worldwide were subjected to cyberattacks1. Less than a year later, the amount of IoT malware increased by no less than 400%2. As IoT adoption accelerates, so does the potential of cyber threats, placing critical industries like healthcare, energy, and manufacturing at heightened risk. Today’s organizations require security solutions that effectively combat these threats while maintaining efficiency in edge environments.
Traditional AI-driven systems, effective in central data centers or WAN configurations, often fall short in edge networks. Looking through data packets to identify threats using neuromorphic AI, inspired by the structure and function of the human brain, offers a transformative solution, by leveraging spiking neural networks to perform event-driven computations, dramatically reducing Size, Weight, and Power (SWaP) requirements.
BrainChip’s Akida 1000 exemplifies this innovation, delivering real-time anomaly detection, ultra-low power consumption, and localized processing. By addressing these edger network challenges, Akida empowers organizations to secure their edge systems without overhauling their infrastructure or compromising performance.
The Growing Cybersecurity Challenge at the Edge
Edge networks face a complex environment: they must process vast amounts of data locally while defending against increasingly sophisticated threats. From advanced malware targeting industrial systems to zero-day vulnerabilities in IoT firmware, attackers are exploiting the inherent limitations of edge devices. These systems often operate with constrained processing power and limited energy resources, making it difficult to implement robust security measures without compromising performance.
Companies of all sizes can experience the consequences of an incomplete cybersecurity strategy, with small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) especially vulnerable. Limited budgets and technical expertise make deploying comprehensive cybersecurity strategies a challenge, leaving their IoT networks potentially exposed. Neuromorphic AI provides a practical solution, offering lightweight, energy-efficient capabilities that address these networkswithout overwhelming costs.
Regulatory compliance adds another layer of complexity. Industries such as manufacturing, agriculture, and utilities must meet strict standards, often while relying on outdated infrastructure. At the same time, remote facilities face operational pressures to maintain uptime despite resource constraints. A proactive and adaptable strategy is required to comply with industry standards without requiring a significant infrastructure overhaul.
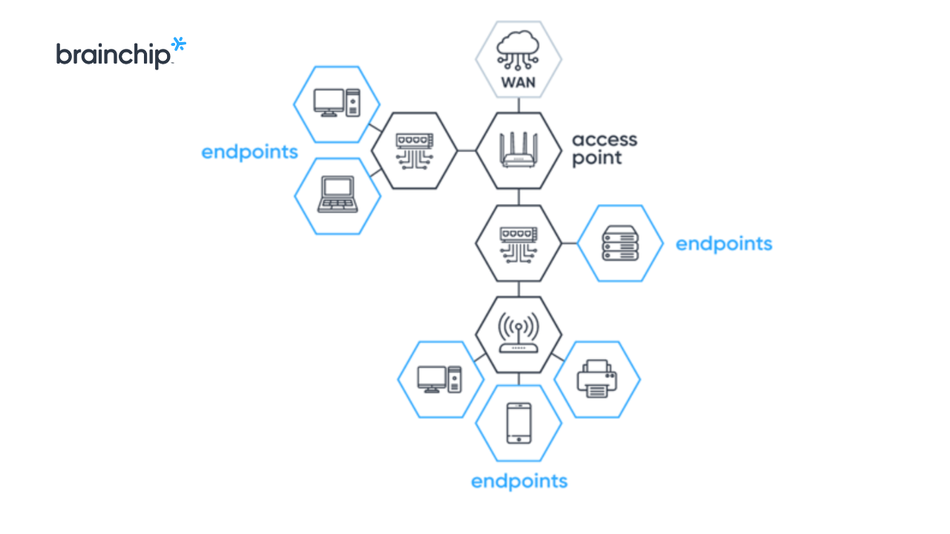
endpoints and for those devices that can incorporate cybersecurity software
and hardware products. Source: Brainchip.
Challenges with Traditional AI Cybersecurity Solutions
Traditional AI-driven security systems often struggle to meet the specific demands of edge environments. While effective in rack based server setups, high-performance GPUs rely on substantial power, space, and cooling infrastructure to function. These requirements are impractical for edge deployments, where devices are typically small, energy-constrained, and designed for lightweight operations. As a result, many edge networks remain exposed to significant cyber threats.
In addition to SWaP constraints, traditional systems introduce latency that hinders real-time threat detection. This delay can be the difference between neutralizing an attack and suffering a critical breach. Remote operations, including agricultural sites, industrial plants, and utilities, further complicate this issue, as they often lack the energy resources and infrastructure necessary to support traditional AI systems.
The limitations of traditional AI highlight why securing edge environments requires solutions designed specifically for their unique constraints. Neuromorphic AI, with its ability to operate efficiently under these conditions, offers a way to overcome these challenges without sacrificing performance or scalability.
How Neuromorphic AI solves these Challenges
Neuromorphic AI represents a fundamental shift in addressing cybersecurity challenges at the edge. Unlike traditional AI systems, neuromorphic systems are designed for energy-efficient, localized operations. This makes them uniquely suited to edge environments where SWaP constraints are critical.
At the core of this innovation is BrainChip’s Akida 1000. Inspired by the human brain, Akida uses spiking neural networks (SNNs) to process data in an event-driven manner, consuming power only when specific data events occur. Its capabilities include:
Real-Time Anomaly Detection: By leveraging event-driven processing and autonomous learning, Akida enables accurate real-time detection of cyber threats. This capability ensures faster response times, reduces the risk of breaches, and enhances the overall security posture of organizations operating in edge environments.
Energy-Efficient Operation: Akida consumes significantly less power than traditional AI systems, making it ideal for energy-constrained applications. Whether deployed in IoT devices, embedded systems, or autonomous platforms, Akida combines low power consumption with adaptive learning and parallel processing to deliver robust cybersecurity without straining energy resources.
Scalability for Large Networks: Akida’s distributed architecture seamlessly integrates new codes and processors, enabling networks to scale naturally. This flexibility supports the growth of large or dispersed systems, ensuring that security measures evolve in tandem with expanding data and infrastructure requirements.
Enhanced Data Security: By processing sensitive data locally on the device, Akida minimizes the need to transmit information to external servers. This approach reduces exposure to interception during transmission and strengthens privacy and data integrity, especially in environments handling confidential or mission-critical information.
Optimized for Edge AI: BrainChip has specifically engineered Akida to fit compact and lightweight designs for edge deployment. Its efficiency-driven architecture and adaptive learning mechanisms enable edge devices to counter cyber threats effectively while lowering operational expenses and infrastructure demands.
These features empower organizations to secure their edge environments without compromising performance or scalability. By addressing the limitations of traditional AI systems, neuromorphic AI delivers a tailored approach to edge cybersecurity that meets the demands of modern IoT networks.
Real-World Applications of Neuromorphic Cybersecurity
The versatility of neuromorphic AI opens the door to a wide range of applications, particularly in edge environments where traditional systems fail to deliver. BrainChip’s Akida 1000 provides lightweight, energy-efficient solutions that address the unique challenges industries and organizations face while operating at the edge.
Enhancing Security in Remote and Isolated Locations
Neuromorphic computing provides innovative ways to improve cybersecurity in remote or off-grid locations, especially in sectors like mining, oil & gas, and agriculture, where energy resources are limited and connectivity is unreliable. Akida’s ultra-low power consumption and localized data processing make it a perfect fit for securing critical operations in these environments, such as safeguarding a mining site’s IoT network or protecting agricultural sensors from intrusion.
Strengthening IoT Deployments
From smart home systems to industrial automation networks, IoT devices are increasingly interconnected, which amplifies their vulnerability to cyber threats. Akida addresses this by enabling localized processing, which keeps sensitive data on the device, reducing the risk of interception. Its compact design and energy efficiency allow it to integrate seamlessly into IoT networks, delivering enhanced privacy and security without compromising functionality.
Benefits of Akida for the Future of Cybersecurity
As we’ve seen, BrainChip’s Akida 1000 offers distinct advantages that position it prominently for edge cybersecurity. Its ultra-low power consumption and compact design make it a cost-effective choice for organizations seeking to secure their systems without the burden of extensive infrastructure investments.
By processing data locally, Akida enhances privacy, reduces latency, and simplifies compliance with stringent regulatory standards. Its modular architecture provides the flexibility to scale security measures seamlessly as operational needs grow, while its adaptive learning capabilities ensure preparedness for future, more sophisticated cyber threats. Together, these benefits demonstrate how Akida addresses current challenges and establishes a robust foundation for the future of edge security.
With the continuous rise of IoT cyberattacks, smart, efficient, edge-specific security solutions like neuromorphic AI empower organizations to protect their critical systems effectively and position them to thrive in an increasingly connected future.
Read more and explore how Akida can be integrated into your system to improve edge AI security.
References
1 Annual number of IoT attacks global 2022 | Statista
2 Report Finds a 400% Increase in IoT/OT Malware Attacks | Zscaler