Aided by AI, New Catheter Design Prevents Bacterial Infections
An interdisciplinary project at Caltech has designed a new type of catheter tube that impedes the upstream mobility of bacteria, without the need for antibiotics or other chemical antimicrobial methods.
This article was first published on
www.caltech.eduThis article was discussed in our Next Byte podcast.
The full article will continue below.
Bacteria are remarkably good swimmers—a trait that can be detrimental to human health. One of the most common bacterial infections in a healthcare setting comes from bacteria entering the body through catheters, thin tubes inserted in the urinary tract. Though catheters are designed to draw fluids out of a patient, bacteria are able to propel themselves upstream and into the body via catheter tubes using a unique swimming motion, causing $300 million of catheter-associated urinary infections in the U.S. annually.
Now, an interdisciplinary project at Caltech has designed a new type of catheter tube that impedes the upstream mobility of bacteria, without the need for antibiotics or other chemical antimicrobial methods. With the new design, which was optimized by novel artificial intelligence (AI) technology, the number of bacteria that are able to swim upstream in laboratory experiments was reduced 100-fold.
A paper describing the study appears in the journal Science Advances on January 3. The work was a collaboration between the laboratories of Chiara Daraio, G. Bradford Jones Professor of Mechanical Engineering and Applied Physics and Heritage Medical Research Institute Investigator; Paul Sternberg, Bren Professor of Biology; John Brady, Chevron Professor of Chemical Engineering and Mechanical Engineering; and Anima Anandkumar, Bren Professor of Computing and Mathematical Sciences.
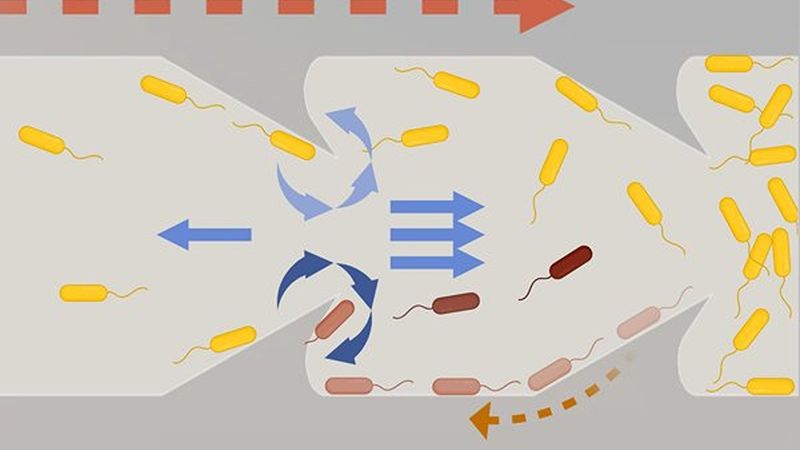
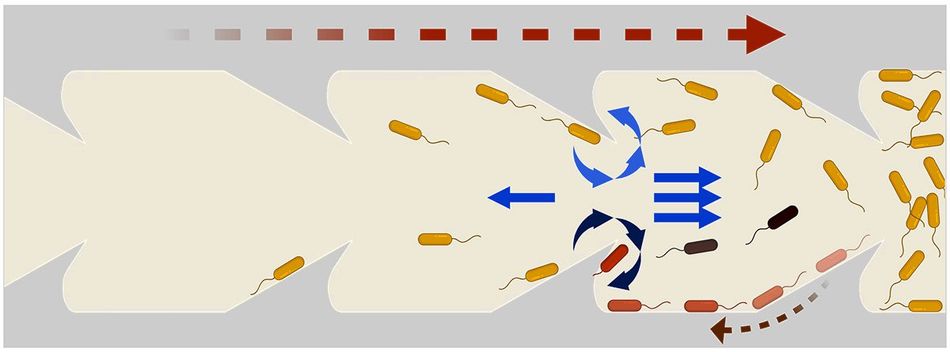
In catheter tubes, fluid exhibits a so-called Poiseuille flow, an effect where fluid movement is faster in the center but slow near the wall, similar to the flow in a river's current, where the velocity of the water varies from fast in the center to slow near the banks. Bacteria, as self-propelling organisms, exhibit a unique "two-step forward along the wall, one-step back in the middle" motion that produces their forward progress in tubular structures. Researchers in the Brady lab had previously modeled this phenomenon.
"One day, I shared this intriguing phenomenon with Chiara Daraio, framing it simply as a 'cool thing,' and her response shifted the conversation toward a practical application," says Tingtao Edmond Zhou, postdoctoral scholar in chemical engineering and a co-first author of the study. "Chiara's research often plays with all kinds of interesting geometries, and she suggested tackling this problem with simple geometries."
Following that suggestion, the team designed tubes with triangular protrusions, like shark fins, along the inside of the tube's walls. Simulations yielded promising results: These geometric structures effectively redirected bacterial movement, propelling them toward the center of the tube where the faster flow pushed them back downstream. The triangles' fin-like curvature also generated vortices that further disrupted bacterial progress.
Zhou and his collaborators aimed to verify the design experimentally but needed additional biology expertise. For that, Zhou reached out to Olivia Xuan Wan, a postdoctoral scholar in the Sternberg laboratory.
"I study nematode navigation, and this project resonated deeply with my specialized interest in motion trajectories," says Wan, who is also a co-first author on the new paper. For years, the Sternberg laboratory has conducted research into the navigation mechanisms of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans, a rice grain–sized soil organism commonly studied in research labs and thus had many of the tools to observe and analyze the movements of microscopic organisms.
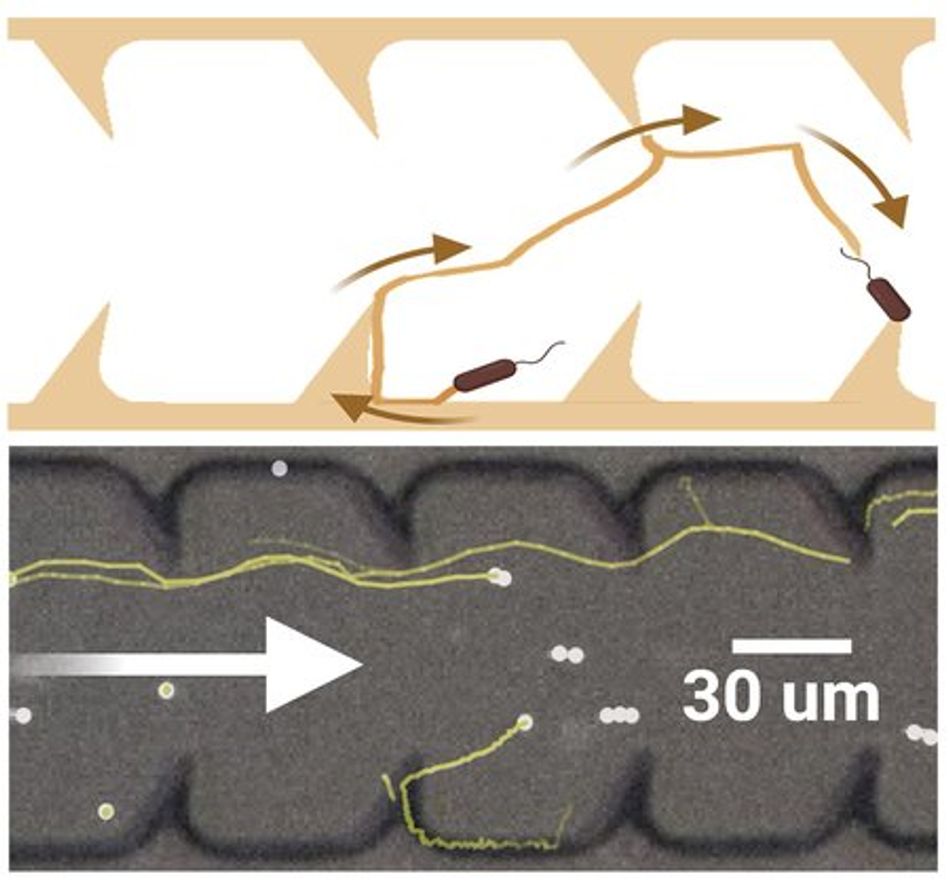
The team quickly transitioned from theoretical modeling to practical experimentation, using 3D printed catheter tubes and high-speed cameras to monitor bacterial progress. The tubes with triangular inclusions resulted in a reduction of upstream bacterial movement by two orders of magnitude (a 100-fold decrease).
The team then continued simulations to determine the most effective triangular obstacle shape to impede bacteria's upstream swimming. They then fabricated microfluidic channels analogous to common catheter tubes with the optimized triangular designs to observe the movement of E. coli bacteria under various flow conditions. The observed trajectories of the E. coli within these microfluidic environments aligned almost perfectly with the simulated predictions.
The collaboration grew as the researchers aimed to continue improving the geometric tube design. Artificial intelligence experts in the Anandkumar laboratory provided the project with cutting-edge AI methods called neural operators. This technology was able to accelerate the catheter design optimization computations so they required not days but minutes. The resulting model proposed tweaks to the geometric design, further optimizing the triangle shapes to prevent even more bacteria from swimming upstream. The final design enhanced the efficacy of the initial triangular shapes by an additional 5 percent in simulations.
"A collaborative spirit defines Caltech," says Sternberg. "Caltech people help each other. This endeavor was truly an interdisciplinary journey, weaving together diverse fields of study."
"Our journey from theory to simulation, experiment, and, finally, to real-time monitoring within these microfluidic landscapes is a compelling demonstration of how theoretical concepts can be brought to life, offering tangible solutions to real-world challenges," says Zhou. "I'm very lucky to be at Caltech with so many talented colleagues."
The paper is titled "AI-aided geometric design of anti-infection catheters." Zhou and Wan are the study's co-first authors. In addition to Anandkumar, Brady, Sternberg, and Daraio, additional Caltech co-authors are graduate student Zongyi Li and alum Zhiwei Peng (PhD '22). Daniel Zhengyu Huang of Peking University in Beijing, formerly a postdoctoral scholar in the laboratory of Tapio Schneider, the Theodore Y. Wu Professor of Environmental Science and Engineering and JPL senior research scientist, is also a co-author. Funding was provided by the Donna and Benjamin M. Rosen Bioengineering Center, the Heritage Medical Research Institute, the National Science Foundation, the Schmidt Futures program, the PIMCO Future Leaders Scholarship, the Amazon AI4Science Fellowship, and Bren Professorships. Stenberg and Anandkumar are affiliated faculty members with the Tianqiao and Chrissy Chen Institute for Neuroscience at Caltech.