Tagged with
healthcare
Latest Posts
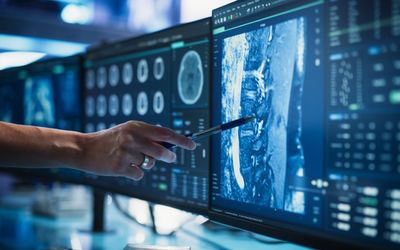
Revolutionizing Digital Healthcare with Axelera AI: Enhancing Patient Care and Operational Efficiency
Healthcare is facing a critical workforce shortage, with AI emerging as a key tool to support clinicians by improving diagnostics, treatment planning, and efficiency without replacing human expertise.
Engineers develop a way to mass manufacture nanoparticles that deliver cancer drugs directly to tumors
Scaling up nanoparticle production could help scientists test new cancer treatments.