A Forward Glance at 5G: Applying Backwards Thinking
Article 1 of our 5G Series: A future of hyper-connectivity requires infrastructure innovation now.
This is the first in an eight-part series exploring 5G. The series will explain key terms and technologies and provide an overview of current and future applications for 5G connectivity.
The articles were originally published in an e-magazine, and have been substantially edited by Wevolver to update them and make them available on the Wevolver platform. This series is sponsored by Mouser, an online distributor of electronic components. Through their sponsorship, Mouser Electronics supports a more connected future fuelled by knowledge and innovation.
Introduction
It was the technology visionary Steve Jobs (1955–2011) who expanded the Danish philosopher Søren Kierkegaard’s (1813–1855) philosophical quote which originally said, “Life can only be understood backward, but it must be lived forwards.” Steve applied this notion to technology saying, “You cannot connect the dots looking forward; you can only connect them looking backward. So you have to trust that the dots will somehow connect in your future.”
Connecting in the Future
Well, the dots of our future are certainly going to be more connected. How they are connected requires backward thinking. Fifth-Generation (5G) wireless technology is ensuring that mobile networks of our future will connect us all. One might say that our future is one of hyper-connectivity in which machines, computers, robots, and people will all interface together.
This article will take a glance at the transformational leap that innovative 5G technology is enabling towards superfast communications, and how key electronic component suppliers are supporting this effort. As engineers, it’s time to put on our thinking caps, turn them backward, and look at how our wireless communication infrastructure requires higher performance to meet the needs of tomorrow.
The Race is On
Being the first to market presents exciting opportunities for businesses. Key network service providers, mobile phone manufacturers, and component manufacturers recognize the necessity to be involved early. Major service providers across the globe have announced their plans to support 5G services, beginning in select cities and rolling out to new cities on a regular basis. Ookla is tracking this rollout which is helpfully captured in this interactive map.
Almost every mobile phone manufacturers, including Xiaomi and Samsung, are offering hardware devices that are set to comply with 5G capabilities. CES 2020 saw a range of devices presented with 5G capabilities that are ready for the commercial market. Telecommunication equipment providers are adapting their products to meet the coming requirements. It will be prudent later to look at how electronic component manufacturers are addressing the changing competitive landscape.
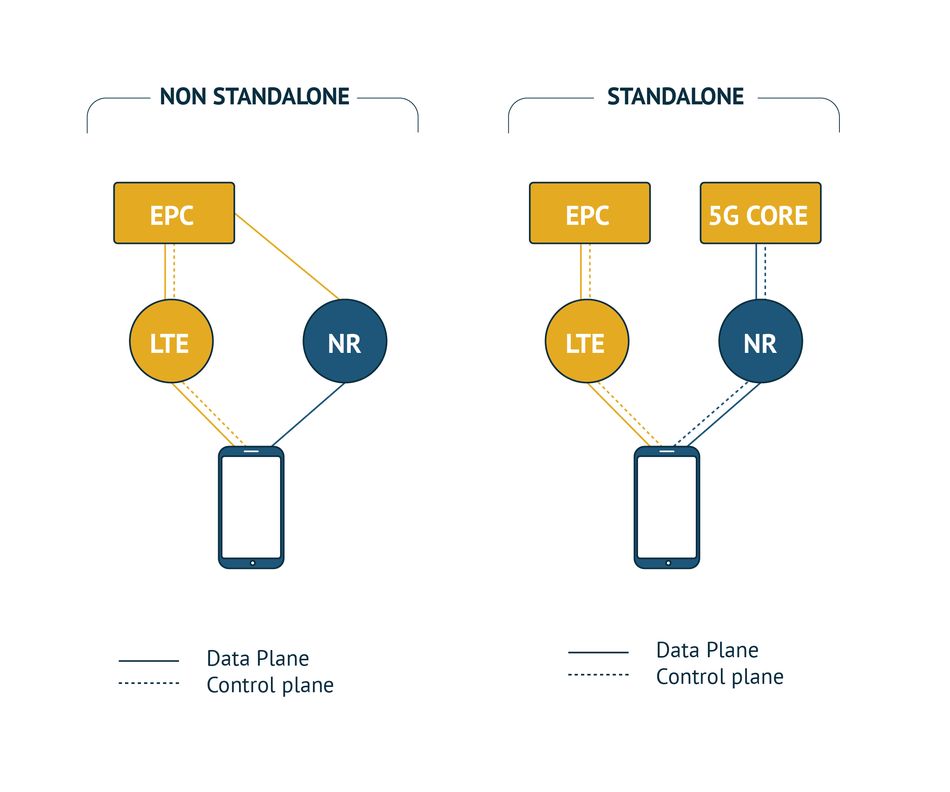
One item requiring tremendous focus is the move from fixed wireless access to 5G mobile non-standalone (NSA) and 5G mobile standalone (SA). NSA will employ 5G mobile built upon a 4G Long-Term Evolution (LTE) core, while SA will receive support from the 5G specific core.
Non-Standalone (NSA) 5G NR
NSA 5G-NR is the early version of Standalone 5G NR mode, in which 5G networks are supported by existing 4G infrastructure. Non-Standalone 5G NR primarily focuses on enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB), where the 5G supported mobiles will use mm-Wave frequencies for increased data capacity but will use existing 4G infrastructure for voice communications[1].
Non-Standalone 5G NR will provide increased data-bandwidth by using two new radio frequency ranges:
- Frequency Range 1 (450 MHz to 6000 MHz) - This band overlaps with 4G LTE frequencies and is called as sub-6 GHz. Bands are numbered from 1 to 255.
- Frequency Range 2 (24 GHz to 52 GHz) - This is the mm-Wave frequency band. The bands are numbered from 257 to 511.
Standalone (SA) 5G NR
3GPP finalized the standalone 5G NR standard in 2018, which will work alongside the Non-Standalone 5G NR standard. Standalone 5G NR will have a new end-to-end architecture that will use mm-Waves and sub-GHz frequencies. This mode will not use existing 4G/LTE infrastructure.
Standalone 5G NR will use enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB), Ultra-reliable and low latency communications (URLLC) and Massive machine type communications (mMTC) to provide multi-gigabit data rates with improved efficiency and lower costs.
The Road Forward to 5G
5G is the natural evolution forward from the presently employed 4G technology. It offers the conceivable potential to handle and administrate three orders of magnitude (103 = 1,000x) more data and information than current technology. This not only represents wireless connections with evolutionary increases but an entirely new level of near-instantaneous connectivity.
While 3G provided users with accessible mobile access to the World Wide Web, 4G has allowed users to be connected socially. However, 5G’s new level of connectivity will enable applications that change the way we live, work, and relax. It will bring forward the dynamic power of the Internet of Things (IoT). This technological revolution will revolve around the wireless infrastructure that will enable new applications such as autonomous vehicles that are capable of driving and navigating obstacles without issues. Industry will change by way of the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), in which robots and industrial automation will be taken to new levels. Work and leisure will change the ability to employ exciting applications such as augmented reality (AR), mixed reality (MR), virtual reality (VR), and extended reality (XR).
Recommended reading: An introduction to 5G
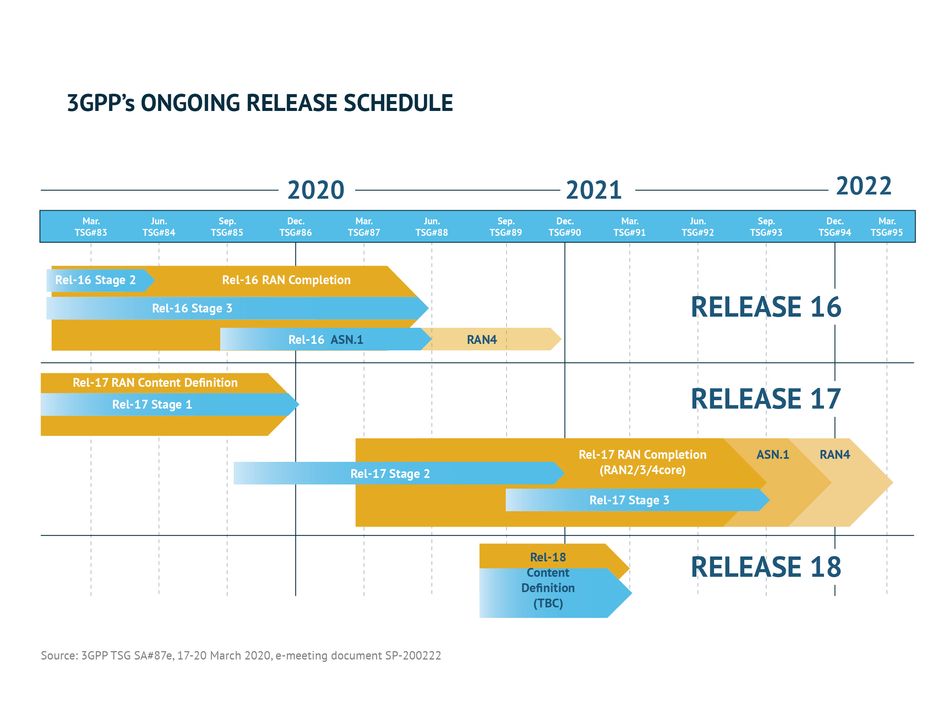
A key to 5G is the group of standards already in place to ensure that this new infrastructure is secure, robust, and highly efficient. The 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP™) organization works to guarantee the effectiveness of these standards. Technical Specification Groups (TSGs) within 3GPP work on issues related to Radio Access Networks (RANs), Service and System Aspects, and Core Network and Terminals (CT). 5G New Radio (NR) specifications are a development that rolled out in late 2017. 5G Phase 1 correlates with Release 15, in parallel with Release 15, is Release 16, which will bring into reality 5G Phase 2.
5G Facts
Let’s now look at some of the specific technical ways that 5G will propel connections forward.
Device Connections
5G’s ultra-wideband capabilities will enhance mobile broadband. It will allow a massively larger amount of devices to connect to the Internet without issues, fueling a dynamic explosion in the IoT. Plans are in place to support a reality that has >1M (>106) devices per square kilometer (km2).
Speed
With much greater connection speeds, 5G potentially promises data rates of 1–10Gbps in contrast to current connection speeds of 50Mbps. Download speeds will also improve.
Latency
Latency - the time delay before a transfer of data begins - will be improved. Reliable, low-latency communications will drop to under 1ms, an improvement at least in an order of magnitude of >101 = >10. Because of low-latency, fast-moving, real-time devices, applications such as self-driving vehicles will have the capacity to locally process, decide, and respond faster than human reflexes.
Spectrum Efficiency
5G’s greater spectrum efficiency, through novel multiple-input and multiple-output (MIMO) antenna and associated technologies, will enable more bits of data to be transferred at specified frequencies.
Power Efficiency
5G’s powerful network processing and control will realize significant gains in its network power efficiencies, enabling more data transfers while lowering energy consumption per data bit transferred. It is expected, despite the high device density coupled with high data streams, that overall 5G network power will be lower than today. This lower power consumption will also extend battery life for devices in the field, ensuring that field replacement issues do not overwhelm users after initial installation.
Throughput
Taken into mutual consideration, all these previously mentioned facts mean that the level of 5G data throughput will explode. High throughput requires high-level infrastructure support to keep things operating smoothly.
5G Components: A Quick Glance at What Is Happening
There is a long list of leading manufacturers who supply the latest products to enable 5G applications. These manufacturers each have different focuses within their efforts to support the arrival of 5G infrastructure. (Note: This list is not comprehensive but is only intended to be representative. The companies have been placed in alphabetical order by company name.)
Analog Devices
Analog Devices has built one of the longest-standing, highest growth companies within the technology sector. Acknowledged industry-wide as a leader in data conversion and signal conditioning technology, Analog Devices also specializes in radio frequency (RF) and power products. The company’s 5G efforts are focused on the development and supply of amplifiers, clocks and timing, data converters, interfacing, isolation, microcontroller units (MCUs), power management, RF, sensors, and wireless connectivity
Intel
Intel stands committed to the growing world of connectivity—from networks, to the cloud, and devices. The organization is investing in the promise of “always-on” 5G connectivity. Intel also offers field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs), systems-on-chips (SoCs), complex programmable logic devices (CPLDs), and complementary technologies, such as power solutions, to provide high-value solutions to customers worldwide. Intel has become a recognized leader in the creation of 5G standards as it transforms purpose-built networks to become more agile, flexible, and scalable with Software Defined Networks (SDN) and Network Function Virtualization (NFV)—setting the stage for 5G expansion. The company is collaborating with an assortment of ecosystem and vertical industry partners to define, prototype, test, and deliver 5G standards and solutions now. From connected cars to AR/VR, smart homes, industrial applications, and cities, Intel delivers unmatched scale, innovation, and expertise to enable next-generation wireless products and services.
Micron Technology
Micron Technology (Micron) is an industry leader in innovative memory and storage solutions. The company’s broad portfolio of high-performance memory and storage technologies—including dynamic random access memory (DRAM), negative-AND (NAND) and negative-OR (NOR) flash memory, and 3D XPoint™ memory—is transforming how the world uses information to enrich lives. Micron’s memory and storage solutions enable innovative trends including artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and autonomous vehicles across key market segments involving cloud, data center, networking, and mobile access. Micron’s 3D-NAND-gate technology is expected to be an asset for data centers. This technology is expected to provide necessary and supporting increases in data storage density, allowing data centers to increase throughput and lower costs. Faster access times also allow the lower latency and high speed of 5G to be more easily realized.
NXP Semiconductors
NXP Semiconductors is a world leader in secure connectivity solutions for embedded applications, NXP is driving innovation in the secure connected vehicle, end-to-end security and privacy, and smart connected solutions markets. The company is a provider of the cellular enablement chipsets and is a founder in many areas of this technology. It will soon be developing and providing a wide variety of digital networking processors, secure interface and system management products, high-performance RF (HPRF) power amplifiers, and smart antenna solutions.
Qorvo
Qorvo is ready today with next-generation RF smarts and solutions to connect people, places, and things faster, further apart, and more reliably. Qorvo is making 5G deployment a reality and is supporting the growth of mobile data with a broad range of RF connectivity solutions. Its robust RF portfolio for both wireless infrastructure and mobile devices include power amplifiers (PAs), phase shifters, switches, integrated modules, and other high-performance RF solutions.
Skyworks Solutions
Skyworks Solutions (Skyworks) is a premier provider of wireless front-end solutions. Skyworks is a member of and key contributor to the industry›s most influential standards organizations, including the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) and 3GPP, where they participate in the development of specifications critical for emerging 5G applications. Skyworks is focused on cellular 5G handsets and the requisite 5G infrastructure. An example of one of their 5G related products is the family of Skyworks Solutions PIN Diode Limiters, developed for use as passive-receiver protectors in wireless or other RF systems.
STMicroelectronics (ST)
STMicroelectronics (ST) offers power management solutions; a large range of microcontrollers, sensors, and connectivity and security solutions; as well as interfaces and transceivers, protection devices, RF front-ends, and analog components. With a strong foundation in silicon carbide (SiC), ST is also moving forward with RF GaN-on-Silicon, enabling future high-performance 5G networks.
TE Connectivity
TE Connectivity provides connectivity and sensor solutions that are essential in today’s increasingly connected world. TE Connectivity believes every connection counts. To support 5G efforts, TE Connectivity is focused on the necessary connectors, relays, passives, sensors, terminals and splices, as well as wires and cabling.
Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments (TI) is a leader in semiconductor solutions for analog and digital embedded applications and processing. Texas Instruments supports 5G efforts with amplifier, clock and timing, data converter, interface, isolation, MCU, power management, RF, sensor, and wireless connectivity products. Some current products that support 5G efforts include the Texas Instruments LMG3410R070 600V 70mΩ GaN Power Stage, and for power management, the LM5045 and LM5036 switching controllers.
Conclusion
The future is certain to be more connected than in the past. 5G wireless technology will ensure that mobile networks of our future will connect us all together. Superfast communications are the transformational leap that innovative 5G technology is enabling, and it›s being brought to realization by electronic component manufacturers dedicated to developing the advanced technologies and products for our future.
This article was originally written by Paul Golata for Mouser and substantially edited by the Wevolver team. It's the first article of a series exploring 5G. Future articles will explore how 5G differs from existing technology and how the potential of hyper-connectivity will be applied in entertainment, smart cities, and industry and how to get there.
Article Two introduces key terms and technologies.
Article Three discusses how systems engineers can evaluate the viability of 5G in the existing connectivity ecosystem.
Article Four examines the relevant standards associated with 5G.
Article Five showcases the radical applications 5G will enable.
Article Six looks at the ecosystems of 5G infrastructure.
Article Seven dives into 5G Antenna Designs.
References
1. https://www.everythingrf.com/community/non-standalone-5g-nr-vs-standalone-5g-nr
About the sponsor: Mouser Electronics
Mouser Electronics is a worldwide leading authorized distributor of semiconductors and electronic components for over 800 industry-leading manufacturers. They specialize in the rapid introduction of new products and technologies for design engineers and buyers. Their extensive product offering includes semiconductors, interconnects, passives, and electromechanical components.