Injection Molding VS CNC Machining VS Urethane Casting, Which Do You Choose
The following article is the differences of Injection Molding, CNC Machining, and Urethane Casting in detail, including processes themselves, manufacturing lead times, relationships of part quantities and cost, materials, the right process in different development stages.

Photo by Daniel Smyth from Pexels
When you develop a new product out of an idea all the way through market, there has always been a need for prototypes, which can be used for design evaluation, testing, proof-of-concept and as bridges to volume production. Injection Molding, CNC Machining and Vacuum Casting are the common manufacturing processes to create the desired parts, whether that is prototypes or end-use parts. However, there are quite a few differences of those processes that should be considered when choosing the right one in different stages of product life cycle.
The following article is the differences of Injection Molding, CNC Machining, and Urethane Casting in detail, including processes themselves, manufacturing lead times, relationships of part quantities and cost, materials, the right process in different development stages. These differences will help you to utilize the strengths and mitigate the limitations of each process in manufacturing your parts.
Manufacturing Process Introduction
Manufacturing Process Differences
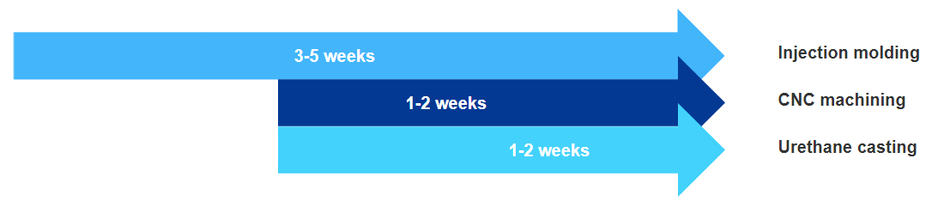
1. Manufacturing Lead Times
Every manufacturing process requires time for production arrangement, machines setting up, surface treatment, packing solutions, delivery, etc. Those factors are predetermined. Factors that are unable to be confirmed, such as the company operational capacities and current workload should be taken into considerations when determining manufacturing process in terms of lead times. Different companies have different manufacturing lead times. However, the following lead times of three manufacturing process can be referred to in general.
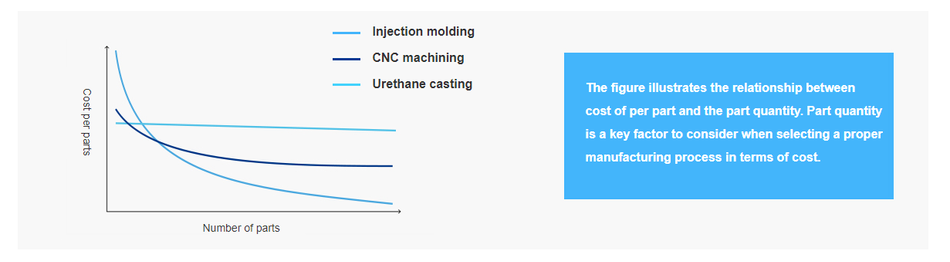
2. The Higher Quantities, the More Costly?
Injection Molding
The total cost of injection molded parts mainly consists of mold cost (aluminum tooling or steel tooling) and the cost for the molded parts. For example, an aluminum tooling usually costs more than a thousand dollars, depending on the complex geometries, materials and finishing options. Part quantities starting from 1,000 pieces for injection molding technology are deemed to be economically. The good thing is that the mold can be used repeatedly. Certainly, mold replacements are required if the part quantities are higher and higher.
CNC Machining
There is no tooling in CNC machining. The single part cost is relatively higher than injection molding cost. The cost of machined parts includes Non-recurring engineering cost (NRE), the raw materials and the manufacturing time and more. NRE cost of CNC machining covers the cost of transforming CAD to CAM, which usually a one-time fee. Raw material is another factor affecting. The complex geometries or the hardened material dominates the manufacturing time, following by the fluctuating manufacturing cost in CNC machining.
Urethane Casting
Urethane Casting is a manufacturing process for low-volume parts out of Urethane Resins. The costs consist of tooling, master pattern, the parts and more. The tooling is usually the silicone material, which can be used for one-time or repeated according to quantities and lead time. 3D printing is usually used to produce the master pattern. This is a relatively economical process for the lower-volume plastic parts, comparing with two other manufacturing processes.
3. What Property of Material Do You Need?
 4. What’s Your Final Goal?
4. What’s Your Final Goal?
Injection Molding
This can be used for a bridge tooling, trial run and low- to mid-volume production before volume production. The proper quantity is ranging from hundreds of parts to thousands of parts. But you must notice that there are certain constraints for part design, including wall thickness, draft angles, undercuts and more. For some manufacturing suppliers, minor modifications on molds are allowed even in this stage in case your design requires iteration. RPWORLD is one of the few manufacturing suppliers that offers such service.
CNC Machining
Do you want the high precision parts with properties of end-use part, part quantity is relatively lower, the lead time is around 1-2 weeks, and the design files are not final. CNC machining is right for your product.
Urethane Casting
Product development is the process of design evolvement. This process is ideal for initial development, such as various testing, new product introduction, pre-sale, crowdfunding and on-demand production. The process is suitable for complex structure like undercut. The fee for modifying the mold is much lower than cost of Injection molding.
Conclusion
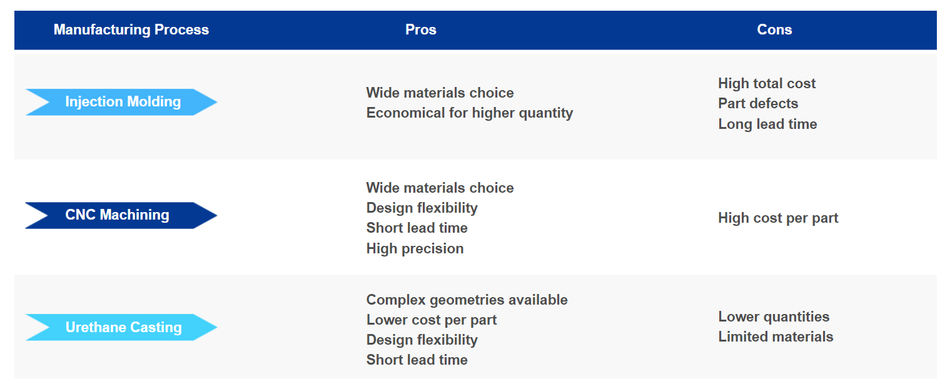
Urethane Casting is often used in the early stage of product development. It is economical, fast and modifiable, and able to simulate the performance of true materials. When you have higher requirements on quantity and quality, your product design is nearly frozen and ready for low- to mid-volume production, injection molding process is the right choice. CNC Machining is ideal to produce small batches and prototypes in which the production of expensive injection molding tools is not feasible. In addition, it machines the parts with high quality and accuracy, can be the end-use parts. A glance at the pros and cons of each manufacturing process:
The practical production of single product is way more complicated than the above. You may wonder: should I be using Urethane Casting, CNC Machining or going straight with Injection molding? But there is no simple answer to use which one, two, or all these processes. A manufacturing expert should be along with the development life cycle of your product. Feel free to contact us for a free design DFM analysis at info@rpworld.com.