What Is CNC Machining? The Complete Basics to Get Started
Computer Numeric Control (CNC) Machining is one of the most popular manufacturing techniques that use automated tools to generate the needed shapes and parts. What is CNC machining or how it works is a common question that anyone associated with the industry should know about. The following text will take a look at the basics of CNC machining and briefly discuss its major applications across different industries.
This article was first published on
www.rapiddirect.comComputer Numeric Control (CNC) Machining is one of the most popular manufacturing techniques that use automated tools to generate the needed shapes and parts. What is CNC machining or how it works is a common question that anyone associated with the industry should know about.
The following text will take a look at the basics of CNC machining and briefly discuss its major applications across different industries.
Overview of CNC Machining
CNC machining, controlled by computers, produces high-precision parts and components. In this process, a computer program controls the movement of the cutting tools, which the program controls to remove material from a workpiece to create a finished part.
CNC machining produces an array of parts and components, including those made from metal, plastic, and other materials. The process can also produce parts with complex geometries and high levels of precision, making it a popular choice for applications in numerous industries, including aerospace, automotive, medical devices, and consumer products.
CNC machining offers several advantages over traditional machining methods, including improved accuracy, consistency, and speed, as well as the ability to produce complex geometries and intricate details. It also allows for the use of advanced cutting tools and techniques, such as multi-axis machining and high-speed machining, which can further improve the efficiency and quality of the process.
The History of CNC Machining
The history of CNC machining can be traced back to the 1940s when the first numerical control (NC) machines were developed. Over time, these machines became more widespread and sophisticated. This gave them the capability to fulfill the requirements of a variety of industries including aerospace, automotive, and defense.
However, older NC machines still needed manual input and had limited capabilities.
This all changed with the advent of computers in the 1970s, which revolutionized the field of manufacturing and gave birth to the first CNC machines. The new CNC Machines came with computer controls and could process information more quickly and accurately. With CNC, operators could input data directly into the machine and the machine would automatically perform the required operations.
This was only the beginning of CNC machines as the technology continued to advance over the years. The development of more advanced software and hardware along with the introduction of new material and tooling options meant more possibilities for manufacturing units.
Today, CNC machines are common in multiple industries and are capable of producing a diverse range of products with high levels of accuracy and precision.
How CNC Machining Works?
Contemporary CNC machines focus on minimizing human intervention as much as possible. This ensures consistent and continuous performance, which facilitates smart manufacturing and delivers excellent results.
However, CNC machining operations require careful consideration from the initial design to the final manufacturing. The entire process works in three different steps:
1 – Design
This is the first step where the deliverables are design files in CAD, CAM, and CAE format. Engineers and designers use CAD/CAM packages that assist them in creating the overall design of the part and product, which is then analyzed for their manufacturability. This analysis, sometimes called DFM (Design for Manufacturing) is an integral process as it ensures maximum benefits at the lowest overall cost while catering to the limitations of the available technology.
In most cases, the CAD tools available in the market come with an internal CAM tool, which facilitates the pre-processing and programming, which is the next step in the CNC process.
2 – Pre-processing and Programming
The primary method of communicating with a CNC machine is through G-Codes or M-Codes. CAM packages generate these codes which are basically the navigating map for the cutting tool in CNC machines.
In most cases, CNC machinists won’t have to intervene in the operations or pre-processing if the design is according to the DFM standards. In case it’s not, some intervention might become necessary to ensure excellent performance.
This is a general step that is common in any CNC machining operation. How much time is needed for the pre-processing is determined by the overall quality of the design process. Programming the G-Codes or M-Codes only need a few minutes.
However, they are dependent on the design. If the overall design is according to the necessary conventions for DFM, the codes would be correct and deliver acceptable results. On the contrary, flaws in the design would result in flawed codes which would naturally deliver unacceptable results.
3 – Machining
The final stage is the actual machining process, which uses the provided codes from the previous step to remove excess material from a block.
Generally, precision machine tools are extremely important but they can’t exactly reproduce the same dimensions as the CAD model. That’s why machinists generally use tolerances, which are different according to the requirements of the industry. The general rule of thumb states precise tolerances would result in higher costs for the manufacturing unit.
Common CNC Operations Across the Industry
The CNC machining process is not monotonous as different operations are depending on the requirement. In some cases, it’s possible to obtain the required shape with a single operation like milling. However, it’s only possible for very simple designs. Generally, the more complex a design is, the more variety of operations it will need.
Here are a few main CNC machining operations that are common across the industry.
CNC Milling
CNC Milling machines operate on the perpendicular axis and use a rotatory cutting tool to create different shapes or products. The process is quite common in multiple industries ranging from automotive, aerospace, medical devices, and other consumer products.
One thing that makes CNC milling process different is workpiece placement. Typically, the workpiece remains stationary and the cutting tool moves around in different directions. The cutting tool moves according to the computer program and removes material accordingly.
The cutting tools can be rotated at high speeds to create precise cuts and shapes, and the machine can be programmed to make multiple passes to achieve the desired final product.
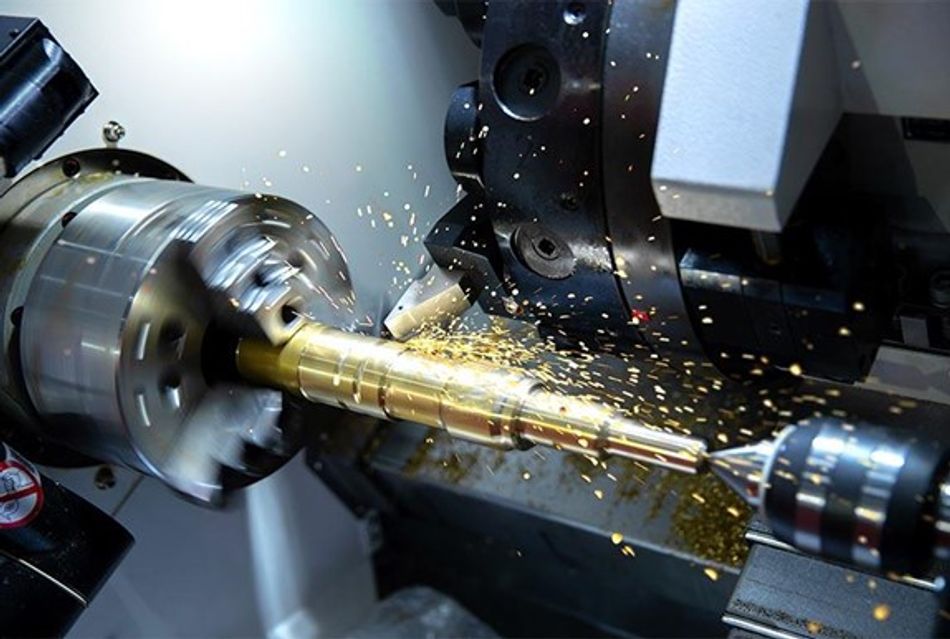
CNC Turning
CNC turning is another integral operation that creates cylindrical parts with high levels of accuracy and precision. The turing process itself is quite simple. Mount the cylindrical part on the machine, which will rotate and the cutting tool would be along the perpendicular and rotational axis.
CNC turning is a common process in the production of different components, including engine parts, shafts, bushings, and gears. The process offers several advantages over traditional manual turning, including increased consistency, repeatability, and efficiency.
There are several types of CNC turning machines, including lathes, turning centers, and Swiss-style lathes. The choice of machine and cutting tool will depend on the specific requirements of the workpiece and the desired end product.
CNC Drilling
Drilling is an important manufacturing process that creates different size holes in a workpiece. The process is completely automated because of the involvement of a computer that precisely controls the movement and speed of the drill bit.
CNC drilling is quite common in many industries including printed circuit boards, metal parts, and plastics. The process offers several advantages over traditional manual drilling, including increased accuracy, repeatability, and efficiency.
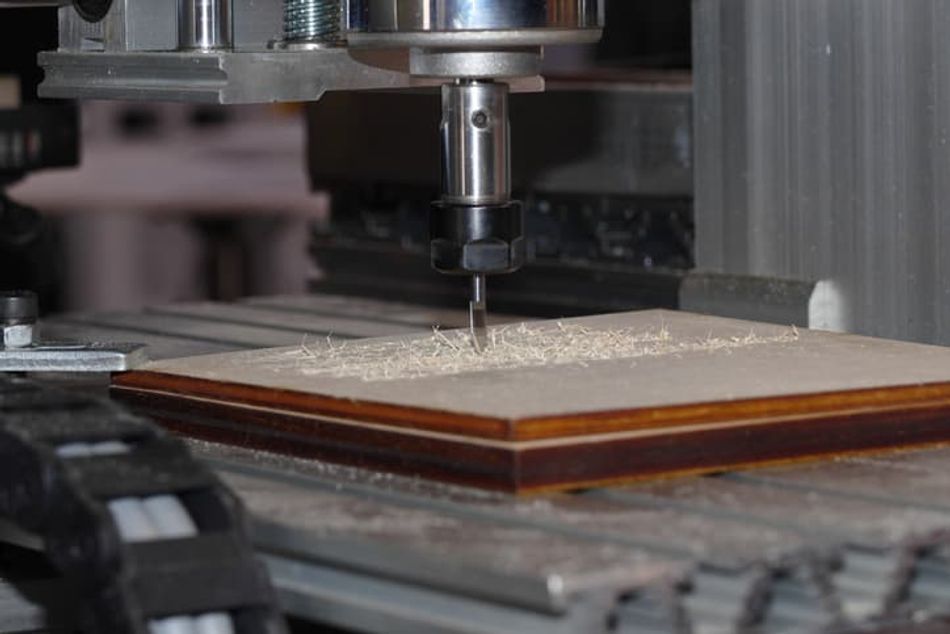
CNC Routing
The crude operations of CNC routers are the same as milling machines. Routers generally deal with softer materials like wood while milling is common for tougher metals. Just like any CNC operation, routers also deliver excellent consistency, efficiency, and accuracy.
In the routing process, the workpiece remains completely stationary while the spindle moves in different directions. Since the routing process is for softer materials, the overall rotating speed of the spindle can be quite low. The types of CNC routing machines are numerous, including benchtop routers, gantry routers, and moving gantry routers. The choice of machine and cutting tool will depend on the specific requirements of the workpiece and the desired end product.
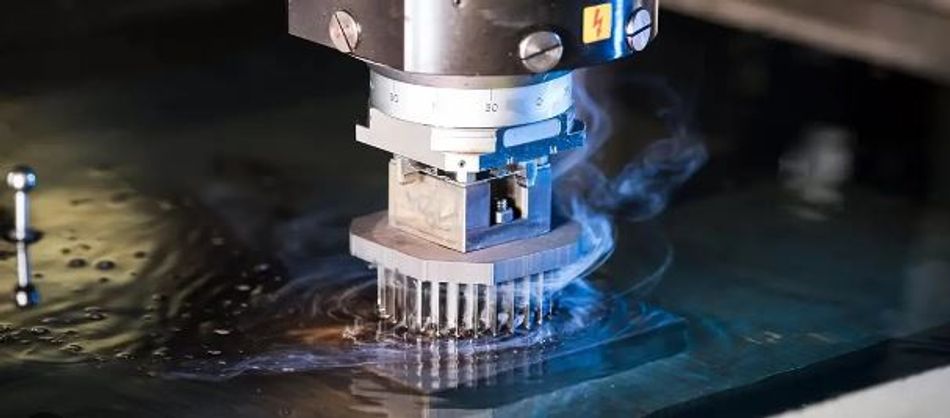
Electric Discharge Machining
An electric discharge machine (EDM) is a manufacturing process that utilizes electrical spark discharges to erode away material and produce complex shapes and geometries.
The process works by creating a spark between an electrode and the workpiece. The machinists submerge the workpiece in a dielectric fluid, which isolates the electrical energy and allows for the precise control of the spark. The spark discharge vaporizes the workpiece and removes access material to obtain the required shape.
There are two main EDM types: sinker EDM and wire EDM. Sinker EDM uses a consumable electrode to create the spark. Contrarily, wire EDM uses a thin wire that moves to and fro to create the spark.
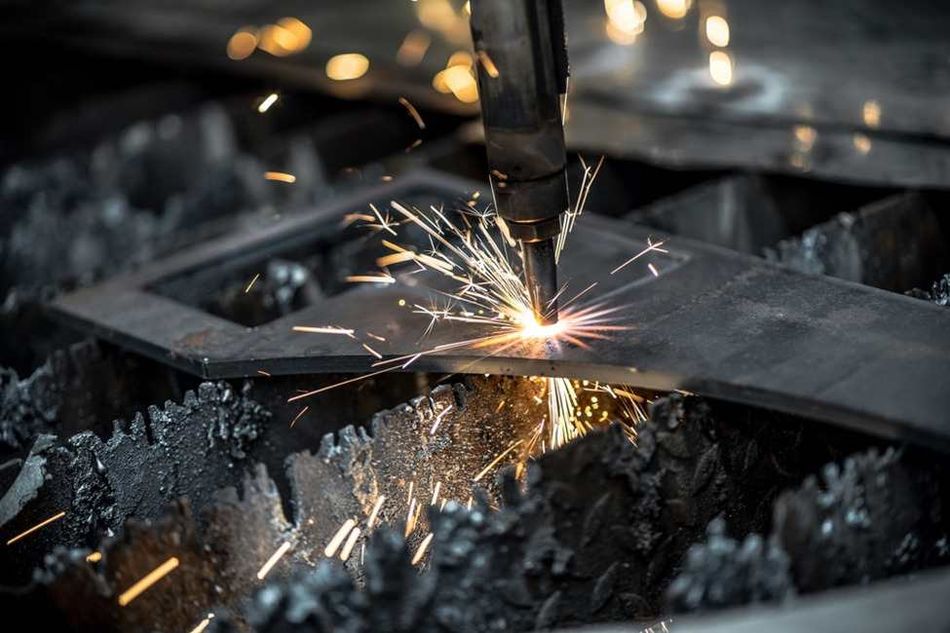
CNC Plasma Cutting
Plasma cutting is a manufacturing process that uses a high-velocity stream of ionized gas (plasma) to cut conductive materials, such as metals. In plasma cutting, a plasma torch generates a plasma arc between an electrode and the workpiece, which has enough energy to cut through the material.
In the next step, the plasma arc melts and vaporizes the material. The process also requires a high-pressure stream of gas (such as air or nitrogen) to blow the molten material away from the cut edge. This results in a clean, precise cut with minimal deformation or discoloration. Thereby, minimizing the requirement for any post-processing.
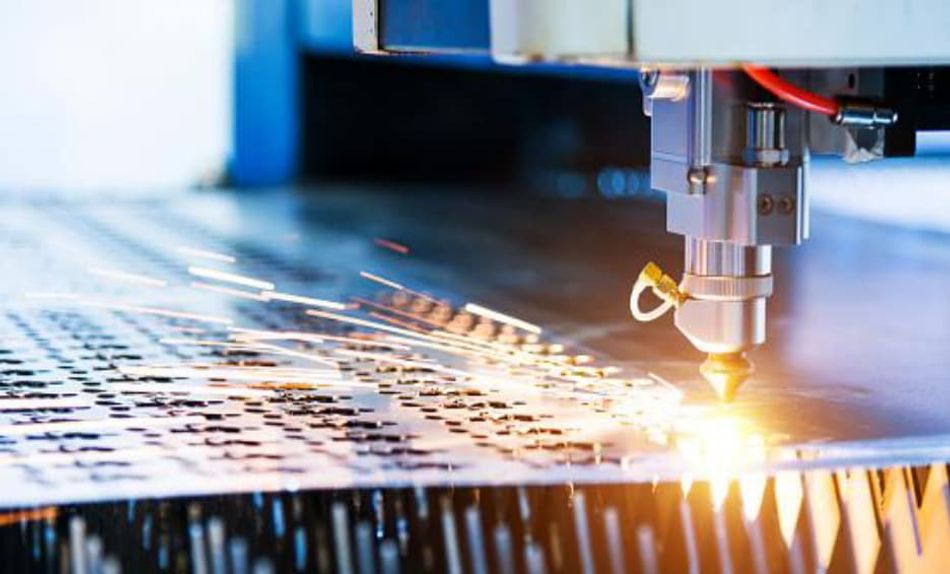
CNC Laser Cutting
This is another common process that’s popular because of its ability to deliver precise and accurate results in the shortest time. The laser for this process is capable of cutting through most of the materials in the industry that’s one of the reasons why it’s common in most industries.
Another reason why CNC laser cutting is so popular is its repeatability. The process works perfectly for large quantities of materials and delivers the most accurate results repeatedly.
Moreover, laser cutting is a very precise process resulting in minimum wastage. Thereby making it ideal for high-value materials common in the aerospace and automotive industries.
Types of CNC Machines
The next question right what is CNC machining is regarding the types of machines. Depending on the overall complexity and cost of the machines, a single machine can perform various operations or can only offer a specific capability.
Here are the most common types of CNC machines that are common in the industry.
- 3 Axis, 4 Axis & 5 Axis Machines
- CNC Routers
- Surface Grinders
- Plasma Cutters
- Laser Cutters
Common CNC Materials and Surface Finishes
CNC machining is a versatile process, but it has its limitations too. Generally, most CNC machines can handle a lot of materials but with varying degrees of precision and accuracy.
Consider the example of Titanium and Aluminum to understand it better. It’s quite difficult to machine Titanium and the results won’t be as precise as they’ll be for Aluminum for the same machines and settings.
Here’s a brief list of common materials that CNC machines generally work with:
- Stainless Steel
- Aluminum
- Titanium
- Copper
- Brass
- Other Steel Alloys
- Plastics
Just like different materials, common CNC machines also offer a few of these surface finishes as well. The following 4 are the most popular in the industry:
- As machined
- Bead blasting
- Powder coating
- Anodizing
- Painting
Common Applications of CNC Machined Parts
CNC machining is one of those manufacturing processes that are not bound by a specific industry or application. Today, these machines are used almost everywhere in one capacity or another. However, the following industries can make the most of what CNC machining offers:
- Aerospace and defense: CNC machining is common in the manufacturing of components for airplanes. Moreover, it’s also used for defense production. For example; weapons, ammunition, and other similar items.
- Automotive industry: CNC machines produce a variety of parts for cars and trucks. Some examples include engine parts, transmission components, and suspension components.
- Medical devices: CNC machining can produce precision components for medical devices such as implants, prosthetics, and surgical instruments.
- Consumer products: CNC machines can produce a variety of consumer products. This includes electronics, toys, and common household items.
- Machinery and equipment: CNC machining is common in producing components for a wide range of machinery and equipment. Some examples include pumps, valves, and gears.
- Prototyping and R&D: CNC machining is often used to produce prototypes and test parts for research and development purposes.
- Jewelry Production: Intricate jewelry requires precision and repeatability that only CNC machining can ensure. That’s why it’s popular in this industry.
- Molds and dies: CNC machining produces molds and dies necessary for producing plastic and metal products.
- Metal fabrication: CNC machining is common in the production of metal components for a variety of industries, including construction, agriculture, and mining.
Main Pros and Cons of CNC Machining
The CNC machining process has its set of pros and cons. Generally, most of the advantages and disadvantages are not industry specific. However, some qualities may have a greater effect on a certain application due to the overall requirements of costs, quality, and time.
Here are the main advantages that CNC machining offers:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Accurate and high precision: CNC machining allows for precise control of the cutting tool, resulting in parts with tight tolerances and excellent repeatability. | High initial costs: CNC machines are quite expensive. Moreover, there are many types of them and most of their operations are not interchangeable. Thereby making capital requirements significant for small and medium businesses. |
| Fast production: CNC machines can operate at high speeds, allowing for faster production of parts. | Trained operators needed: Unlike traditional machines, CNC operators require significant training before they can start working. Which means they are more in demand and have higher wage requirements. |
| Enhanced capability: CNC machining ensures consistent quality, which is excellent for a consumer product or large-volume production. | Increased material wastage in some cases: While efficient, some CNC operations may waste more material compared to the manual process. However, the precision, repeatability, and efficiency they offer may offset this con in many cases. |
| Complex design: CNC machines can be programmed to produce a wide variety of parts. From simple to complex shapes, everything is possible with the right design considerations and machining approach. | |
| Consistency and low human error: CNC machining ensures consistent quality, which is excellent for a consumer product or large-volume production. | |
| Cost-effectiveness: CNC machining can be cost-effective for large production runs. Larger production runs utilize economies of scale to reduce the overall cost per piece, which is exactly what the industry demands. | |
| Improved safety: CNC machines are significantly safer than their manual counterparts. Generally, the operators control the machine from another room, which keeps them safe from shards, heat, and exposure to other threats. | |
| Reduced maintenance requirements: Since most of the processes are automatic, they are optimized to perform consistently without any intervention. Thereby lowering the overall maintenance requirements. |
RapidDirect: The Right Manufacturing Partner for Every CNC Project
Setting up and maintaining CNC machines requires significant resources that small or medium businesses can’t spend. That’s why opting for CNC machining partners is a common industrial practice that circumvents this issue.
RapidDirect is a perfect manufacturing partner that provides the very best when it comes to CNC machining. The company operates from China, which is a global hub for manufacturing and has a long history of delivering excellence.
The expert team at RapidDirect has the capability to deliver tolerances down to 0.01mm and provide all services including but not limited to CNC turning, CNC milling, plasma cutting, laser cutting, etc. Apart from that, RapidDirect also has an ISO 9001 certification and a state-of-the-art quality control process that always ensures customer satisfaction.
Bonus: What’s It Like to be a CNC Machinist?
Being a CNC machining is not easy. It’s a tough and demanding job requiring a lot of creativity, dexterity, and quick thinking. Moreover, CNC machining is evolving and it’s the machinist’s job to keep up with the new updates and deliver the best the current technology has to offer.
Here are the few expectations that come with the role of a CNC operator:
- Hands-on knowledge: It’s important to understand the inner working of the machines and perform basic diagnostics. CNC machinists spend a lot of time with different cutting tools and need excellent hand-eye coordination.
- Technical skills: A basic level of understanding of machine tools, fixtures, and design philosophies is critical.
- Problem-solving: CNC operations are automated but may encounter any issues as well. The operator must know enough basics to deal with the problem and rectify basic issues easily.
- Programming skills: The only way to communicate with a CNC machine is through the program. So, it’s necessary for a CNC machinist to have the necessary programming knowledge.
- Attention to detail: Precision is a basic requirement for any CNC machining project and any operator must have the right attention to detail for the best performance.
Conclusion
What is CNC machining and why is it so popular are some common questions that many unassociated with the industry ask. In essence, CNC machining is one of those processes that drive the current industrial age and have a huge role to play in the future as well.
Concepts like SMART factories and Industry 4.0 manufacturing won’t be possible without CNC machining as it allows manual machining interfaces to interact with computers and then ensure precision with consistency.
While incredible, CNC technology has some limitations as well. However, those are negligible considering the advantages and there are high chances that the current issues will be addressed as the technology improves with the passage of time. Try the best CNC machined results, contact RapidDirect today!