AI at the Edge Report. Chapter 1: Wi-Fi Analytics Services Enabling Edge AI
Intelligence at the Edge: Bringing AI Closer to You
Our new report, AI at the Edge: Technology Accelerated by Wi-Fi Services, dives deeply into the convergence of Wi-Fi services and Edge AI and explores how a technology model like WaaS can accelerate the adoption of AI at the edge.
Below is an excerpt from Chapter 1 of the report. To read the full report, including in-depth case studies, download it now.
Typically, artificial intelligence has been powered by cloud computing, given AI’s need for computing power and data-intensive processing. However, with the advent of edge computing, the AI landscape has been shifting, allowing for the rise of Edge AI. Edge AI is a revolutionary approach to how we deploy AI in various application areas, as it enables local computing and processing of data. That means the computing power is brought closer to the source of data, facilitating on-device data processing. With Edge AI, the system can make decisions in real time and with full contextual awareness by enabling AI features and capabilities directly on devices. Such a process would benefit from significant advantages brought about by Edge AI, including quick response, high bandwidth efficiency, and cost-effectiveness, to name a few.
Unlike Cloud AI, which relies on remote servers for data processing and analysis, Edge AI is applied locally among a spectrum of devices spanning from data centers to IoT endpoints. The nature and location of the data being processed determine whether Cloud AI or Edge AI is more suitable for a particular application. For processing-intensive applications where latency can be compromised for the sake of in-depth data analysis and powerful computation, Cloud AI would be the ideal option. However, many applications are time-sensitive and require real-time data processing and prompt responses. This is where Edge AI takes center stage, minimizing the need to send data back and forth to a cloud server. This can take place at any location denoted as the edge, such as retail stores, hospitals, traffic lights, autonomous vehicles, and educational facilities.
The following table explains the benefits and applicability of Edge AI and Cloud AI and how they differ from one another. Keep in mind that Edge AI and Cloud AI are not interchangeable technologies but rather applicable in different applications and scenarios. In fact, Edge AI and Cloud AI can even be complementary for systems that include both time-dependent and processing-intensive applications, which can benefit from a hybrid approach to data processing that integrates both technologies, as we’ll discuss later in this report.
Table 1: Applicability and Benefits of Edge AI and Cloud AI
The Evolution and Adoption of Edge AI
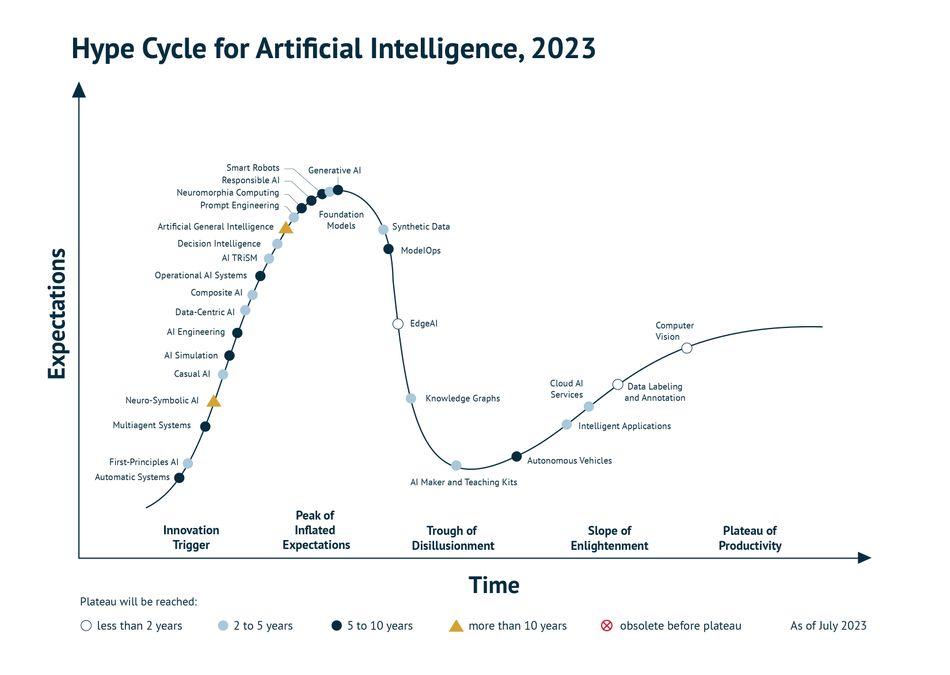
A 2023 report by Gartner on innovations in and around AI has highlighted the AI hype cycle for this year, showcasing the various advancements in AI and where they are today in terms of the public’s expectations . Among these innovations, we can see Cloud AI slowly navigating the so-called “Slope of Enlightenment” stage, where it is gradually transitioning toward mainstream adoption. In fact, Gartner expects Cloud AI to become mainstream in two to five years. Meanwhile, one of the fastest-growing innovations we can pinpoint on the cycle graph is Edge AI, showing a fast adoption rate to reach mainstream productivity in less than two years. This validates the potential that Edge AI has demonstrated in the past 2-3 years and shows that both edge and cloud computing can support AI applications in a symbiotic manner in the very near future.
The recent developments in Edge AI have opened up new opportunities for devices to operate with human-like intelligence, regardless of their location. The successful deployment of AI models at the edge can be attributed to innovations that have significantly contributed to today’s digital transformation. For instance, neural networks and AI infrastructure have reached a level of maturity enough to pave the way for generalized machine learning. Organizations are now able to train AI models and deploy them in production at the edge. Besides, the recent advanced Edge AI accelerator chipset development, such as Axelera Metis, with high performance and low power budget, has made it possible to integrate these AI capabilities at a low power budget and with very high inference speed. Relay2 is pioneering this embedded integration with Wi-Fi Access Point, the edge of the Wi-Fi network. This is further strengthened by the widespread adoption of IoT devices, which is arguably the key reason behind the blowup of big data. Businesses can now collect every type of data from various sources. This availability of data and corresponding devices has made it possible to deploy AI models successfully at the edge.
Given their remarkable ability to process and comprehend a range of unstructured data, including visuals, audio, temperature, language, faces, and more, AI algorithms have emerged as effective solutions for problems that end users face in real-time. Yet, deploying these AI applications primarily in centralized data centers like the cloud may prove impractical, especially with concerns about latency, bandwidth, and privacy. This is where the benefits of edge applications can facilitate AI deployment with their localized nature and decentralization, enabling real-time insights, high availability, and enhanced privacy.
Nonetheless, Edge AI is not free of limitations, either. It still faces challenges, especially in data management, integration, security, miniaturization, and scalability. To overcome these challenges, a harmonious and purposeful co-design of hardware and software is necessary, and coordination with other technologies can prove quite fruitful. In fact, one of the most promising solutions for Edge Intelligence comes in the form of the convergence of Edge AI with cloud-based Wi-Fi Services, as we’ll see in the following section. Achieving miniaturization, model accuracy, energy efficiency, and cost-effectiveness simultaneously is a complex challenge. However, with proper coordination, optimization, and communication, we can facilitate the emergence of the next set of AI advancements at the edge.
Next-Level Intelligence: Reinforcing Edge AI with Wi-Fi Services
Since its inception about two and a half decades ago, Wi-Fi has shown significant development and adoption, with connection speeds skyrocketing from a few megabits to multi-gigabits per second. With this increase in speed, we have also seen an exponential rise in Wi-Fi-enabled devices, with almost every mobile device and computer now including Wi-Fi by default. In order to support the growing usage, demands, and throughputs of Wi-Fi, the network architecture has played a crucial role. Initially, Wi-Fi deployments were based on standalone access point architectures but later shifted to centralized hardware-based controller architectures. However, along with Wi-Fi functionalities like network optimization and mobility came some challenges, including scalability, reliability, manageability, and bottlenecks in performance, especially with increasing Wi-Fi traffic and link speeds. To tackle these challenges, service providers like Relay2 have been harnessing the power of the cloud and enabling vendors to shift from on-premise hardware controllers to cloud-native wireless controllers. Such a cloud-native system can provide the same benefits of centralized management without the constraints of physical hardware or associated adaptations. This not only enables greater flexibility but also offers more efficient and cost-effective management and coordinated control. As a result, this space has allowed for the rise of Wi-Fi-as-a-Service (WaaS), a subscription-based service that integrates software, infrastructure, and managed services to enable centralized management and coordinated control across different access points and automation of network monitoring and troubleshooting.
Bringing Wi-Fi services and Edge AI into the same picture, we can see how their benefits align, where Wi-Fi enhances Edge AI’s scalability and integration capabilities, and Edge AI furthers the user experience of Wi-Fi solutions with data-driven insights and real-time analysis. For instance, looking at Edge AI’s integration challenges, we can still see cases of incompatibility stemming from differences in hardware, software, and communication protocols, which result from the unique architecture, specifications, and interface of every edge device. Employing Wi-Fi at this level enables secure, wide-coverage wireless communications, which further promotes interoperability and minimizes compatibility issues. Similarly, scalability challenges in terms of how Edge AI systems are handling increasing amounts of data and devices may compromise efficiency. The adaptability and scalability brought about by Wi-Fi services can help overcome these hurdles by enlarging a business’s network infrastructure and enabling effortless infrastructure management to meet the growing demand and shifting requirements.
In other words, tying wireless and edge computing together can empower AI applications and reshape the business landscape to drive the digital transformation we are experiencing today. This convergence of Wi-Fi and edge computing presents a promising frontier for innovation, efficiency, and growth. As companies continue to recognize the value of this convergence, we can anticipate a marked increase in its adoption. As a result, edge computing would bring about a new wave of intelligent AI applications by integrating more computing power, which would allow adaptive learning and real-time responsiveness. This would be a significant step towards a more resilient system as the demand for always-on services continues to grow across various industries and application areas, including education, smart buildings, intelligent traffic management, smart agriculture, and smart retail. As more companies embrace the convergence of Wi-Fi and edge computing, we can expect to see a new era of technological innovation and efficiency.
Right at the center of this technological fusion is Relay2, a leading Wi-Fi service provider that is on a mission to challenge the status quo of today’s Wi-Fi access point market. Relay2 is at the vanguard of the Wi-Fi edge-computing revolution, powered by their innovative ServiceEdge Platform, a Service Points technology that provides unparalleled performance, scalability, security, and privacy across a wide range of edge applications. In the next chapter, we will dive deeper into Relay2’s Wi-Fi services and explore how Relay2 is poised to reshape the Wi-Fi industry and how its patented platform is enabling more AI applications and capabilities within the edge-computing framework.
This was an excerpt of Chapter 1 of the AI at the Edge: Technology Accelerated by Wi-Fi Services report. To read the full report, including in-depth case studies, download it below.
Read excerpts of the other report chapters:
Chapter 2: Relay2 and Edge AI
Chapter 3: Applications & Case Studies
Chapter 4: Future of Edge AI with Wi-Fi Technology





