Direct Drive vs Bowden Extruder for 3D Printing
Understanding the differences and benefits of direct drive and bowden extrusion systems.
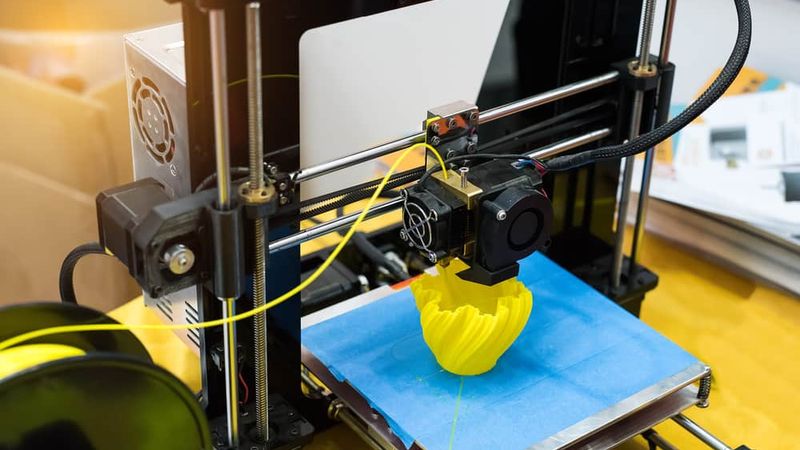
Direct drive extruders feed the filament directly into the printhead using a stepper motor and drive gears.
Not all Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) 3D printers are the same. Some are based on a Cartesian system, others are based on the Delta model. Some have open print beds, while others have enclosed print chambers. And some utilize direct drive extrusion, while others use a bowden system. These different choices can initially seem overwhelming—after all, how should you know what’s the best option for your 3D printing needs if you’re new to the technology—so we want to help demystify them. Today, we’re looking specifically at direct drive vs bowden extrusion systems to understand how each works, how they differ, and what their respective benefits are.
To start things off, it’s first important to understand how FDM 3D printers are set up. If we look at the basic components of a desktop 3D printer, you’ll find the build platform, the printhead (where the melted filament comes out of the nozzle), and the extruder (which is responsible for feeding filament into the printhead). Whether we’re talking about a direct drive or bowden system, the extruder always consists of at least a motor and drive gears, which control the filament’s movement through the printhead. The placement of the extruder and the feeding technique are what distinguish direct drive from bowden. Let’s dive in.
Direct Drive Extrusion
In the case of direct drive extrusion, the extruder is mounted directly onto the printhead. This means that the filament is fed directly into the printhead, and the extruder moves with the printhead along the machine’s axes as it prints. The proximity of the extruder to the nozzle has the benefit of promoting consistent extrusion as well as retraction, which can lead to superior print outcomes in terms of filament precision. Another consequence of mounting the extruder directly onto the printhead is that the extruder does not require a particularly powerful stepper motor, since the filament is not traveling far from the gears to the nozzle.
Direct drive extrusion is best suited for Cartesian and CoreXY 3D printer styles. These machines have the stability to support a heavier printhead. In some cases, the additional weight of the extruder on the printhead can inhibit print speeds and mobility due to increased vibrations.
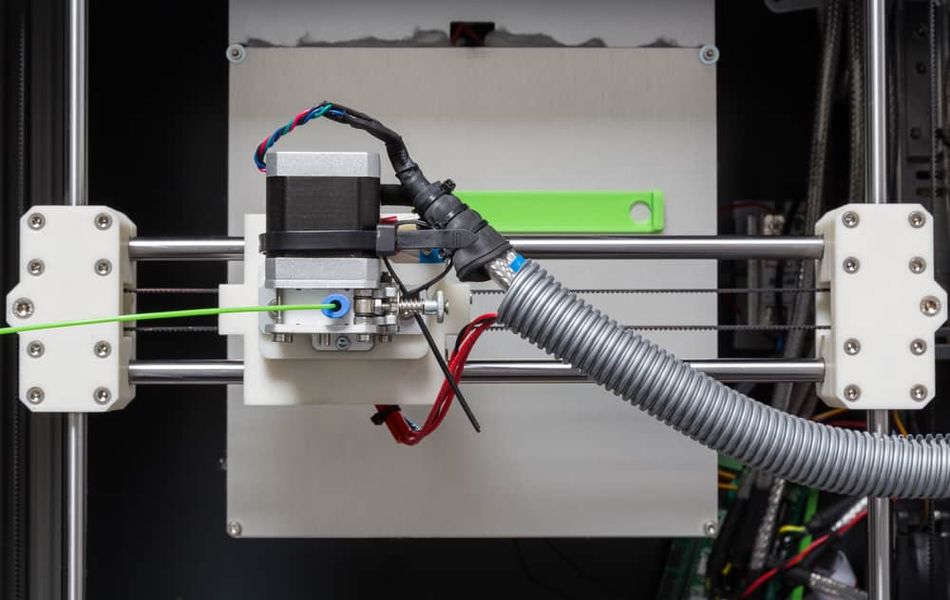
Advantages of Direct Drive Extruder
Delivers consistent extrusion thanks to the placement of the extruder on the printhead. Because the gears are positioned right above the nozzle, there is better control over extrusion and retraction.
The proximity of the extruder to the printhead also requires less motor power to feed the filament compared to the bowden extruder setup.
Direct drive extrusion works well with flexible materials as well as carbon fiber filament and other fiber-reinforced materials.
Disadvantages of Direct Drive Extruder
One of the main cons of direct drive extrusion is that mounting the extruder onto the printhead adds substantial weight to the mobile printhead. This added weight can lead to greater vibrations, which can negatively impact the quality of your final print.
The weight of the direct drive extrusion systems can also impact print speeds.
Direct drive systems can make 3D printer maintenance more difficult, as it is harder to access parts within the printhead, such as the nozzle.
Recommended reading: TPU print settings explained
Bowden Extruder
A bowden extruder, or bowden tube extruder, is an extrusion mechanism that is mounted to the frame of an FDM 3D printer as opposed to the printhead. From its higher position, the bowden extruder feeds 3D printing filament from the spool through a PTFE tube (aka the bowden tube) into the printhead. The purpose of the tube is to keep the filament stable as it is fed into the printhead. Typically, the bowden tube diameter should not be much greater than the diameter of the filament. This ensures that the filament does not bend or flex as it is fed through. (Tubing for 1.75 mm filament is usually 2 mm in diameter, although it may be beneficial to use 1.9 mm or 1.85 mm tubing.)[1]
The primary benefit of the bowden extruder is that it places the weight of the extruder onto the frame, resulting in a lightweight printhead, which can move along the printer’s axes with ease. It is also worth noting that using a bowden tube may require extra maintenance, such as cleaning.[2] If filament particles build up in the bowden tube, it can lead to problems like under extrusion.
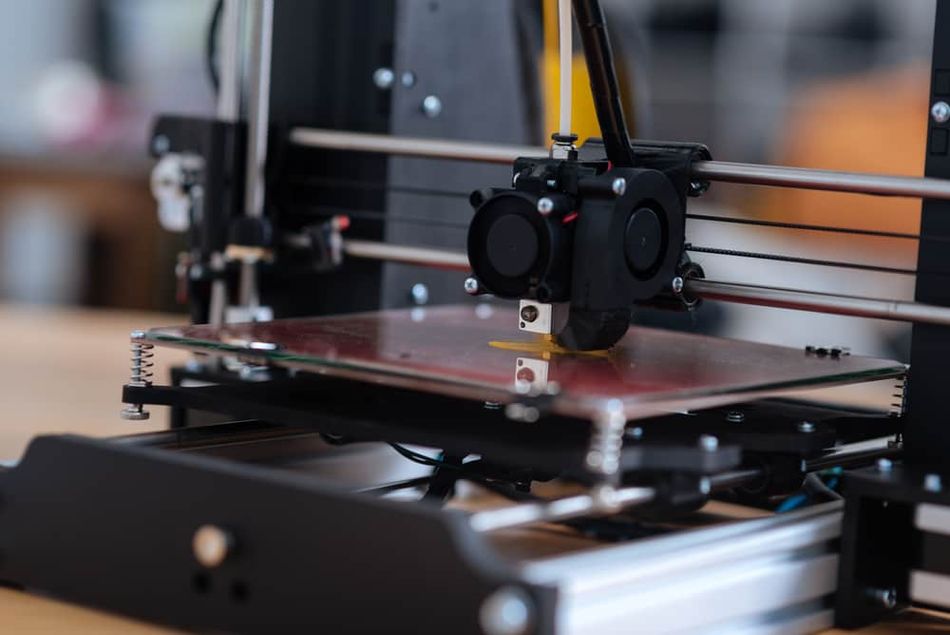

Advantages of Bowden Extruder
Works well with PLA filament and can help minimize stringing.
As a lightweight extrusion system mounted on the printer’s frame, the bowden system promotes fast printing speeds, smooth printhead motions, and can result in higher quality prints.
The smooth movement of the printhead with a bowden extruder can minimize 3D printing problems such as ringing and ghosting.
A better option for Delta-style 3D printers, which are less stable than Cartesian 3D printers.
Allows for easier maintenance of printhead components, such as cleaning or replacing the hot end.
Disadvantages of Bowden Extruder
Bowden extruders are not as suitable for flexible or fiber-filled abrasive filaments.
Because of the distance between the drive gears and the nozzle, the bowden extruder requires greater torque from the stepper motor to feed the filament. In other words: a more powerful motor is needed.
Bowden extruders are less responsive due to friction within the bowden tube. Retraction settings must account for this.
The bowden tube can wear down with repeated retraction in the 3D printing process, which can eventually lead to melted filament oozing out into the extrusion system. Using a heat break to create a buffer between the bowden tube and the hot nozzle can help mitigate this.[3]
Recommended reading: How to fix under extrusion: Maintenance and print settings
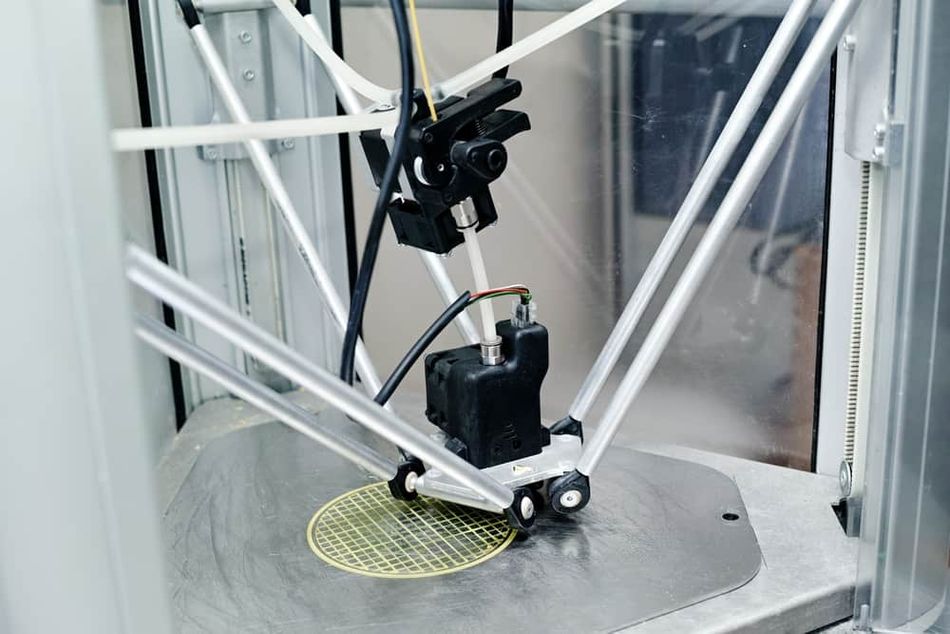

Direct Drive System vs Bowden System - which one to use?
When it comes down to it: there are pros and cons to both types of extrusion system. It really just depends on what your 3D printing priorities are. If you are interested in working with a range of filaments, such as flexible TPU and fiber-filled materials, then it’s safe to say a direct extruder is probably your best option. If you are primarily printing PLA, ABS, or another standard filament and print speed is a priority, then a bowden tube is likely the way to go.
The type of 3D printer you are working with is also an important consideration. Cartesian printers as well as CoreXY machines tend to have more stable frames and motion control than Delta 3D printers. This means their printheads are better suited to handle the additional weight of the direct drive extrusion system. Delta printers benefit from less weight on the printhead and are thus a better match with bowden extruders. That being said, new direct drive extruder models are more lightweight and are thus more versatile.
Recommended reading: 3D print ghosting causes and potential solutions
Key Takeaways
When getting started with FDM 3D printing, it’s important to understand the different types of extruders that are out there. As we saw in this article, direct drive and bowden tube extruders are the two most common varieties. Here are the key takeaways from what we covered:
Both direct drive and bowden extrusion systems use a stepper motor and drive gears to feed filament (push and retract) into the 3D printhead.
The key difference between the two extrusion systems is that direct drive extruders are mounted onto the printhead, while bowden systems are mounted onto the printer’s frame.
Direct drive extruders offer better extrusion and retraction control and the stepper motor requires less power to feed the filament into the printhead.
Direct extrusion works well with most filaments, including flexible filaments and fiber-filled materials.
Bowden extruders use a tube to feed the filament from the extruder to the printhead. They enable faster, smoother printing (less wobble) because there is no added weight on the printhead.
Bowden extruders are more suitable for Delta 3D printers, which have less stability than Cartesian machines.
References
[1] Hardy, Will. “Bowden vs Direct Drive Extruder”. E3D. November 2022. [Accessed January 2023]. https://e3d-online.com/blogs/news/bowden-vs-direct-drive
[2] “How to clean the Bowden tube”. Ultimaker Support. November 2022. [Accessed January 2022]. https://support.makerbot.com/s/article/1667411551738
[3] 3D Printing Canada. “DIRECT DRIVE VS BOWDEN TUBE”. Youtube. August 2022. [Accessed January 2023]. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QfENVzM7Krw
