Can Retinal Scans Help in Predicting Myocardial Infarction?
The proposed AI system has an accuracy between 70% and 80% that can be employed as a second referral mechanism for cardiovascular examination.
![Retinal Scans to Predict Cardiovascular Diseases [Image Credit: University of Leeds]](https://images.wevolver.com/eyJidWNrZXQiOiJ3ZXZvbHZlci1wcm9qZWN0LWltYWdlcyIsImtleSI6IjAubnJwcXYxZnR5ZFJldGluYWxTY2Fuc3RvSWRlbnRpZnlIZWFydERpc2Vhc2UucG5nIiwiZWRpdHMiOnsicmVzaXplIjp7IndpZHRoIjo4MDAsImhlaWdodCI6NDUwLCJmaXQiOiJjb3ZlciJ9fX0=)
Retinal Scans to Predict Cardiovascular Diseases [Image Credit: University of Leeds]
Medical examinations are primarily based on observing associations and building hypotheses to determine the flow of medical investigation and treatment. With the introduction of deep learning models, researchers have found a way to bring medical imaging to medical discoveries. However, several factors make it difficult to improve accuracy due to a wide range of parameters like patterns, values, colors and shapes associated with real data.
Retinal images have already been in practice by ophthalmologists to diagnose and monitor eye disease. The extension of medical imaging diagnosis for cardiovascular diseases has been a key strategy to reduce CVD prevalence in the popular. Cardiovascular imaging has always been secondary care due to the cost, making it difficult for developing and underdeveloped countries to adopt. But the significant association of retinal microvascular abnormalities with systemic and cardiovascular diseases has made retinal images a routine in ophthalmologic practice.
The research article published under Nature Biomedical Engineering, “Prediction of cardiovascular risk factors from retinal fundus photographs via deep learning,” [1] shows that analysis of retinal images has enabled the prediction of cardiovascular risk factors like age, gender, smoking status and blood pressure. Extending the line of research led by the University of Leeds designed an artificial intelligence system that can process retinal images to predict the risk of myocardial infarction.
Deep Learning Leads the Way for Predicting Myocardial Infarction
In the paper, “Predicting myocardial infarction through retinal scans and minimal personal information,” [2] the researchers reported the use of retinal images in the early identification of heart diseases. The implementation of a deep learning model to analyze eye scans will result in identifying patients at high risk of a heart attack. Along with retinal scans, relevant patient metadata has been used to estimate left ventricular mass (LVM) and left ventricular end-diastolic volume (LVEDV).
According to Professor Alex Frangi, the University of Leeds, “cardiovascular diseases, including heart attacks, are the leading cause of early death worldwide and the second-largest killer in the UK.” “This technique opens up the possibility of revolutionizing the screening of cardiac disease. Retinal scans are comparatively cheap and routinely used in many optician practices. As a result of automated screening, patients who are at high risk of becoming ill could be referred for specialist cardiac services.”
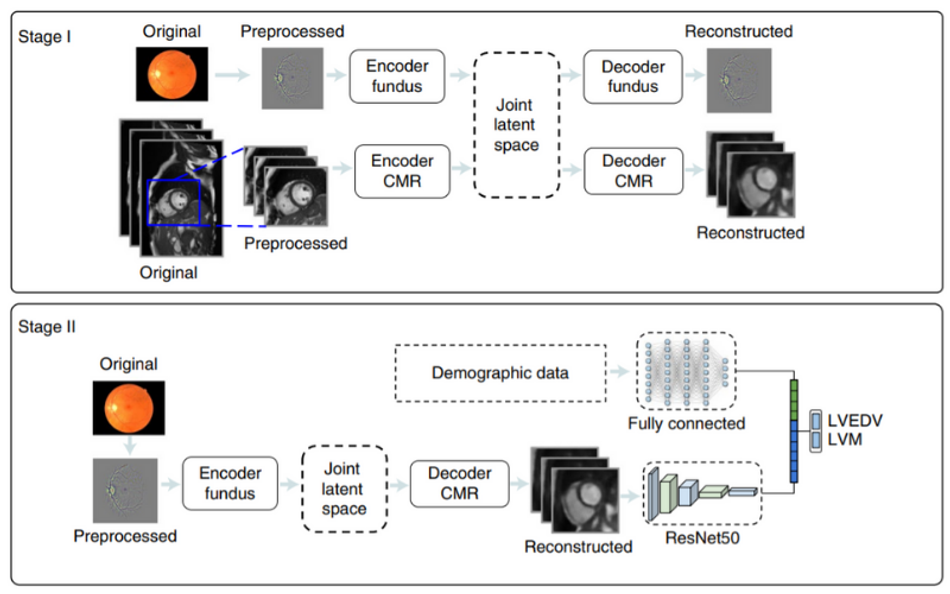
The deep learning approach uses a multichannel variational encoder and a deep regression network. For the multichannel variational encoder, the design shows two pairs of encoder/decoders to train the network with retinal and CMR images. In stage 1 of the proposed method, a joint latent space is created between the two channels of retinal and CMR images to result in a reconstructed image. In stage 2 of the overview diagram, the deep regression network is trained on the reconstructed image and demographic data to estimate the LVM and LVEDV.
After deep learning networks were trained on retinal and cardiac scans of more than 5000 people, the AI system could estimate the size and pumping efficiency of the left ventricle from the retinal scans only. When there is an increase in the size of the ventricle, it suggests an increased risk of heart disease. Along with the size of the left ventricle and pumping efficiency added with the patient’s metadata, the AI system makes a prediction about the risk of heart attack over a period of the next 12 months.
Is it a reliable method of medical imaging?
To get a fair comparison between the proposed method and state-of-the-art methods, the initial experimentation included manual and automatic delineations [3] of the CMR images to estimate the LVM and LVEDV. All the results are presented in Bland-Altman and Pearson’s correlation plots. The proposed AI system has an accuracy between 70% and 80% that can be employed as a second referral mechanism for cardiovascular examination. With this research article, the use of deep learning in the analysis of retinal images can revolutionize the investigation methodology for regular screening of heart patients.
“The AI system is an excellent tool for unraveling the complex patterns that exist in nature, and that is what we have found - the intricate pattern of changes in the retina linked to changes in the heart,” says Sven Plein, British Heart Foundation Professor of Cardiovascular Imaging at the University of Leeds.
All the algorithms used in the proposed method are publicly available.
References
[1] Poplin, R., Varadarajan, A.V., Blumer, K. et al. Prediction of cardiovascular risk factors from retinal fundus photographs via deep learning. Nat Biomed Eng 2, 158–164 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41551-018-0195-0
[2] Diaz-Pinto, A., Ravikumar, N., Attar, R. et al. Predicting myocardial infarction through retinal scans and minimal personal information. Nat Mach Intell 4, 55–61 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s42256-021-00427-7
[3] Attar R, Pereañez M, Gooya A, Albà X, Zhang L, de Vila MH, Lee AM, Aung N, Lukaschuk E, Sanghvi MM, Fung K, Paiva JM, Piechnik SK, Neubauer S, Petersen SE, Frangi AF. Quantitative CMR population imaging on 20,000 subjects of the UK Biobank imaging study: LV/RV quantification pipeline and its evaluation. Med Image Anal. 2019 Aug;56:26-42. DOI: 10.1016/j.media.2019.05.006. Epub 2019 May 25. PMID: 31154149.
