Industrial Communication Protection for RS-485 and Ethernet
Article #5 of our Circuit Protection Series: Ports like RS-485 and Ethernet are a key part of any communication system but can be vulnerable to stress.

This is the 5th article in a 7-part series examining circuit protection. The series examines the challenges of high-speed circuit protection, as well as the many products and solutions used to solve them. This series is sponsored by Mouser Electronics, an online distributor of electronic components. Through their sponsorship, Mouser Electronics shares its passion for technologies that enable a safe and connected world. This article was authored by Craig Morrow and Todd Phillips with editing from Paul Golata.
Industrial communication requires a high-reliability operation, which means protecting industrial communication equipment is extremely important. In the following article, we’ll discuss aspects of RS-485 and Ethernet connections and provide some application examples. After that, we will look at some considerations depending on what kind of environment you might find yourself operating in. Finally, we will then examine some potential electrical threats, and then finish with some solution examples.
Two of the most common industrial nodes are Ethernet and RS-485. Ethernet has surpassed RS-485 in choice for most applications for several key reasons. First, Ethernet runs up to 1GB/s, while RS-485 is limited to 10MB/s. Further, Ethernet can Power over Ethernet (PoE), which enables power to the field device. In contrast, RS-485 can transmit longer distances, up to approximately 1500m, while industrial Ethernet is limited to about 100m.
This then begs the question: Where would design engineers favor the employment of RS-485 versus Ethernet? In general, designers would want to use Ethernet when one has a lot of data transmission. For example, in security cameras or machine vision systems. But choosing RS-485 makes sense where there are long transmission links such as remote I/O or other things you need to get out in the field, such as energy metering.
Location, location, location
Where and how one industrial communication node is employed is critical to understanding how to provide port protection. If the line is outside (even for only a section), there needs to be an awareness of the risk from lightning. In applications with long-distance runs, an understanding of the potential of inductive surge risks must be considered. Additionally, wherever a human might touch something related to the system, you need to be aware of electrostatic discharge (ESD) in the interfacing. Additionally, acknowledging the potential for a motor’s stop and start to cause fast electrical transients is necessary.
Specific design considerations
There are several specific challenges that the designer must take into account. For example, lightning surges and induced power surges can impact ports that you want to protect. ESD, from human contact, is also a risk to consider. Additionally, inadvertent miswiring or an improperly connected cable can cause damage to equipment by sending too much voltage or current. Fast electrical transients can arise when someone stops or starts a big motor or other kinds of equipment. These transients are often called bouncing. Finally, one often might experience problems if and when cables wear into a break, and they can send wrong power to a port. These issues can be addressed or reduced by wire ties and other methods that can minimize through-the-system vibrations.
RS-485 Protection
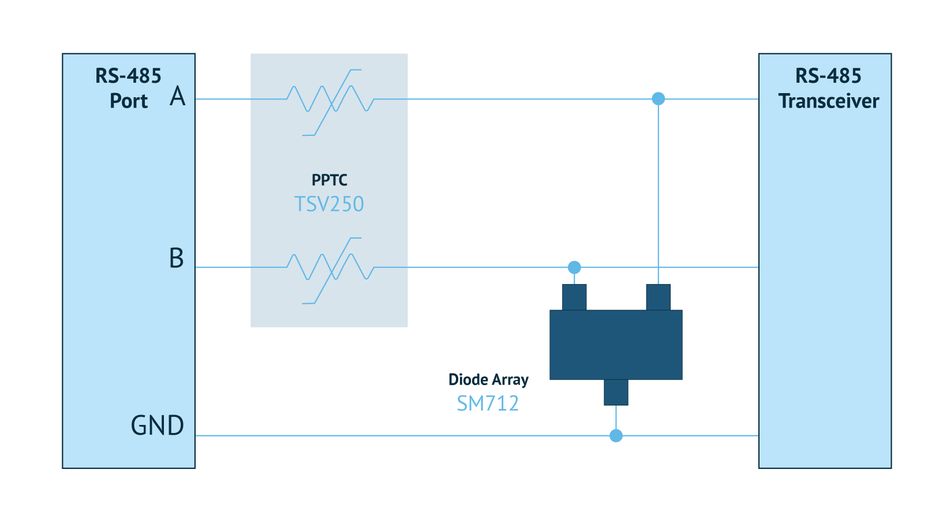
RS-485 is commonly employed in buildings (Figure 1).There is a wide variety of products and technologies that provide intra-building protection. A resettable polymeric positive temperature coefficient (PPTC) can protect against both short circuit and power crosses. For voltage protection, TVS Diode arrays are suitable.
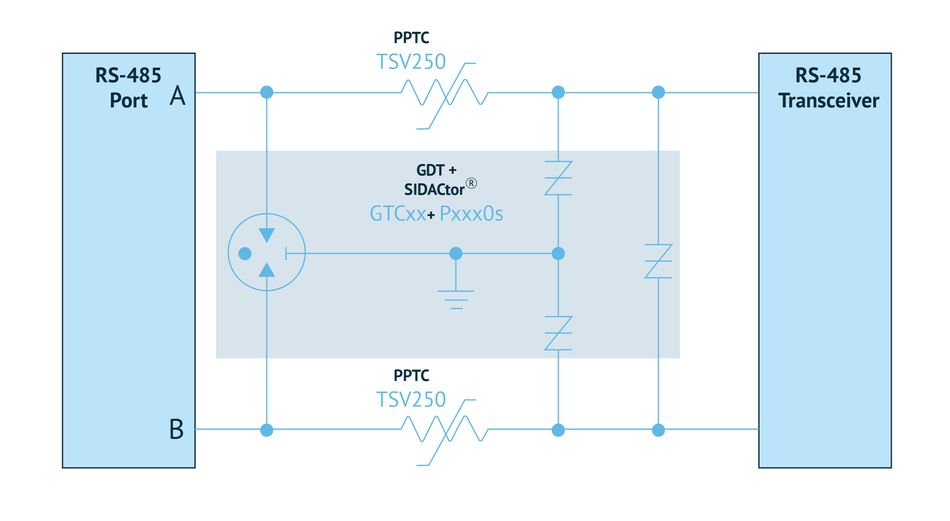
If the solution is not within the building but rather outdoors and in a harsher environment, different protection solution needs to be considered.(Figure 2). Resettable PPTCs to protect against short-circuit and power crosses may be employed. For lightning protection, a combination of a a gas discharged tube (GDT) with a thyristor. In the event of a lightning surge a thyristor will fire quickly. This will cause more voltage across the PPTC and, at that point, the GDT will fire. The resistance of the PPTC must be selected carefully for proper coordination with the GDT.
Ethernet Protection
Let’s now look at Ethernet solutions in the same contextual environments. For intra-building protection, one can generally use a simple diode array (Figure 3). This will provide port protection from electrostatic discharge and fast electrical transients, and when this is used in an application where lightning is not a concern. One of the advantages of this TVS diode array is its low capacitance, which enables high transmission speeds. If one needs data speeds of greater than 1GB/s per second, one will need to employ additional twisted pairs.
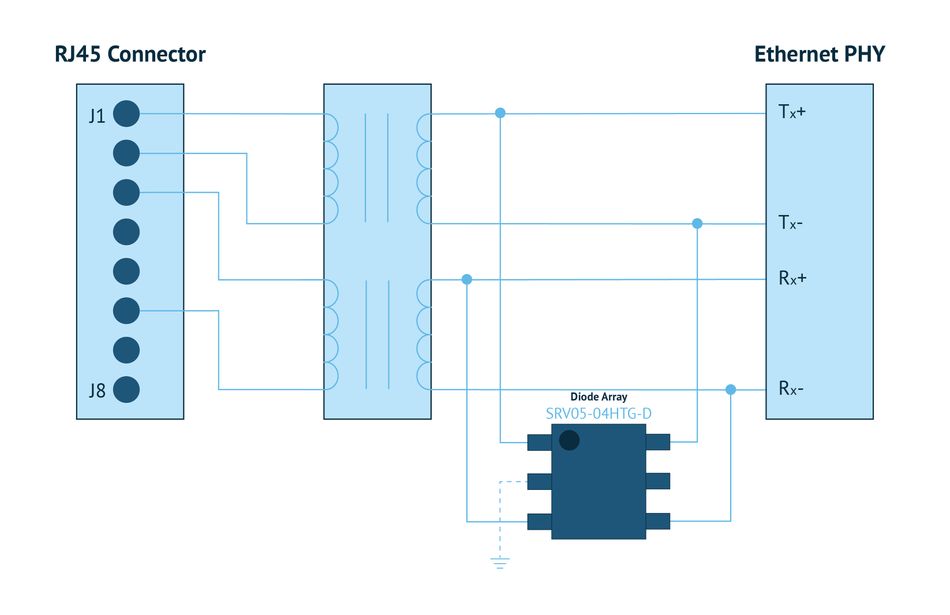
Figure 3: Ethernet Port Protection (Image: 04. Ethernet Port Intra-building)
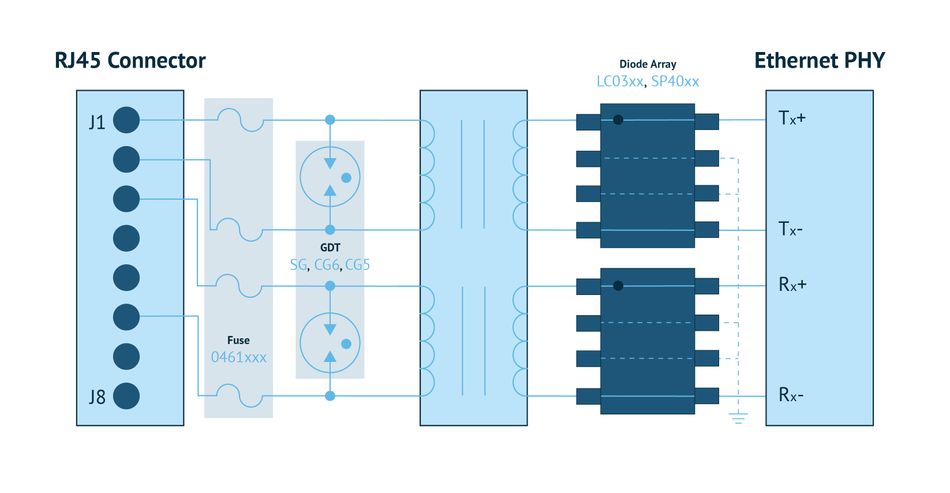
When going outdoors with Ethernet into a harsh environment, additional protection is required (Figure 4) that includes fuses specifically designed for high-speed telecom applications. These niche solutions require only one fuse per wire pair. For protection against lightning, GDT with a diode array is the recommended choice. The class ratings will determine what specific protection you need. For example, if you need four kilovolts and two kilohms.
PoE Protection
Power over Ethernet (15.4W), PoE+ (30W), PoE++ (90W)) powers remote devices via the Ethernet cable (Figures 5). Designers again deploy specific fuses for these applications. For voltage protection, a TVS diode should be used. TVS diodes can be used across the center tap signal pair and a second one across the center tap spare pair. The TVS diode can be chosen based on one’s search needs for the specific application.
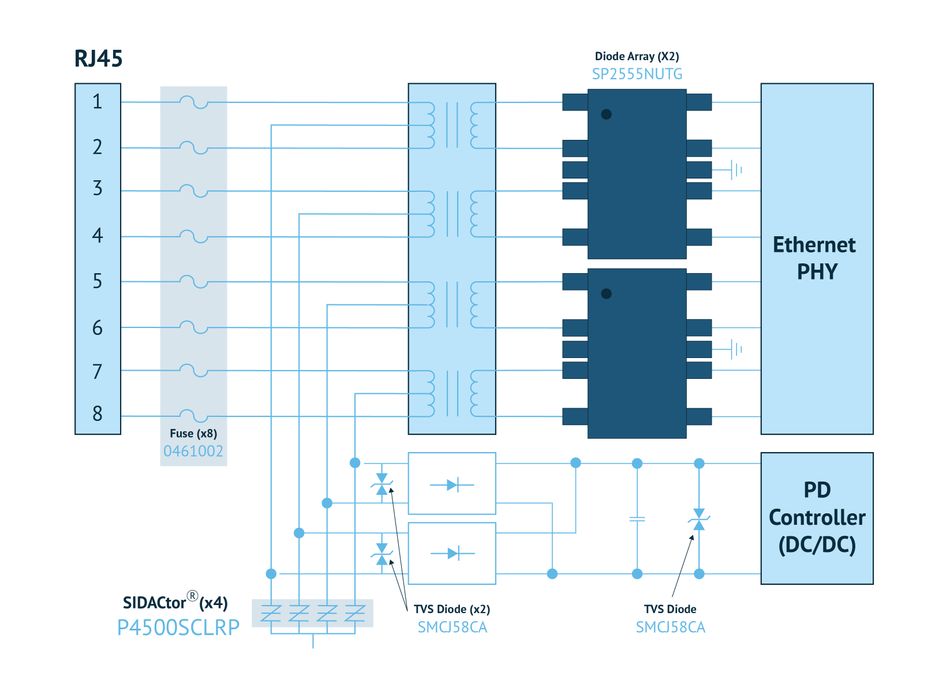
For any Ethernet application, the optimal protection depends on where it’s being used and the amount of exposure that that location might have to electrical hazards. Standard GR-1089 provides an excellent reference to what testing could be done to select the right components and know that one has adequate protection. One of the tests, GR-1089, requires a power cross test in how the circuit is protected. It requires a solution such as the 461 fuses, which can not only protect for a power cross event as a short circuit type of event but would also be able to withstand the surge levels that are adequate for that outdoor connector. SIDACtors provide surge protection on the lines that have the power. Ghost power created on PoE gets separated off and fed into a power controller to be used as real DC power, and those lines are protected primarily by a SIDACtor.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, we can see that the importance of industrial communication protection cannot be overstated. Designers must be engaged with the potential risks to ports from the early stages of design and take into consideration location and application when making decisions.
This article was initially published by Mouser and Littlefuse in an e-magazine. It has been substantially edited by the Wevolver team and electrical engineer Fahad Farooq. It's the fifth article of a 7-part series examining circuit protection. Future articles provide an overview of how to protect wired communication, the change of USB standards, and the importance of protecting against electrical stress in industrial automation environments.
Article one gave an overview of general ports.
Article two introduces electrical stress.
Article three took a closer look at USB-C protection.
Article four highlighted the issues with USB fast-charging.
About the sponsor: Mouser Electronics
Mouser Electronics is a worldwide leading authorized distributor of semiconductors and electronic components for over 1,100 manufacturer brands. They specialize in the rapid introduction of new products and technologies for design engineers and buyers. Their extensive product offering includes semiconductors, interconnects, passives, and electromechanical components.

References:
https://eu.mouser.com/Semiconductors/Interface-ICs/RS-485-Interface-IC/_/N-45lyy
https://eu.mouser.com/Power/Power-Supplies/Power-over-Ethernet-PoE/_/N-axgm1
https://eu.mouser.com/Semiconductors/Communication-Networking-ICs/Ethernet-ICs/_/N-5cfym