Quadruped robot with advanced front flipping mobility
Advanced mobility and modular functions allow complex moves such as front flipping.
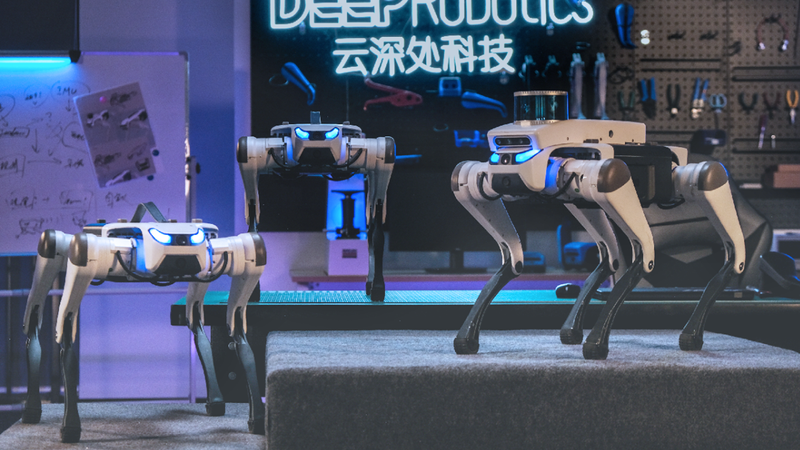

Lite3: new technology for increased strength, agility, mobility, speed, navigation, and endurance
One of the newest versions of its dexterous intelligent robot dog, Lite3, has now launched in Europe. It combines advanced mobility and an open modular structure for education, research and innovative entertainment.
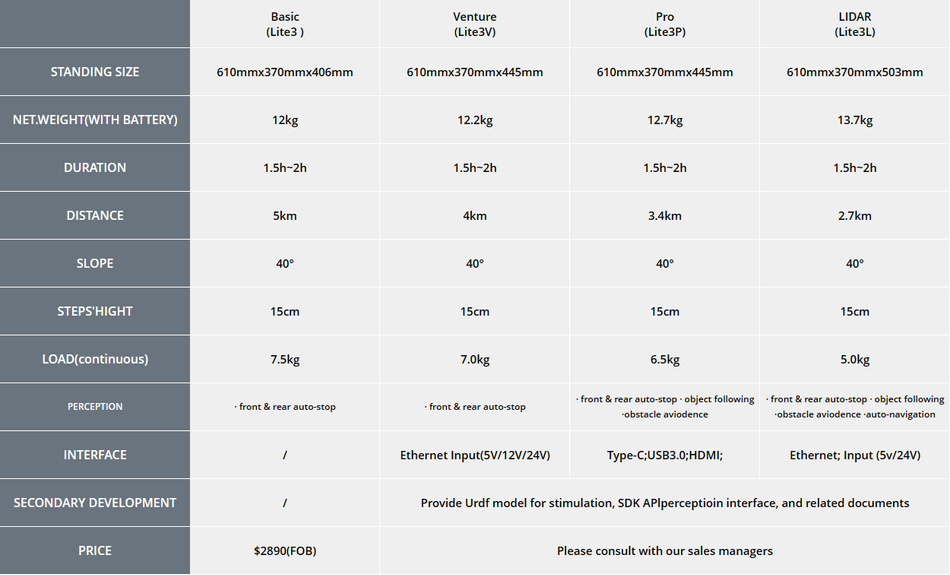
The new Lite3 series offers four product models: a basic model designed for technology enthusiasts; and three more advanced versions intended for scientific study purposes. With new features that include DEEP Robotics’ latest proprietary limb joints, control systems and advanced algorithms, Lite3 has a more powerful, quick and durable movement capability. It also offers robust scalability that can be ramped up by installing more modules.
Major design upgrade
The new version incorporates significant technological advances on Lite2. The latest robot dog has proprietary leg-joint technology that provides far greater strength and drive, with torque increased by 50%. The high-torque joint drive module offers extremely high torque density, response bandwidth and reversed transmission efficiency, enhanced rotation stability, and less power consumption.
The payload of Lite3 is 40% greater than that of its predecessor. It can carry loads of up to 7.5 kilograms. Its endurance in terms of time and range has nearly doubled. The Lite3 can operate for up to 90 minutes and has a range of 5km.
The Lite3 features an industrial-level real-time control system with depth optimization, a first for the product lineup, with overall computing power increased threefold. The Lite 3 can climb steps up to 15 cm in height, close to the current maximum for a quadruped robot of its size, and runs at a peak speed of 4ms-1. It can also perform horizontal jumps, high jumps, front flips and other similarly difficult manoeuvres. The algorithm upgrades make its movement more agile and responsive.
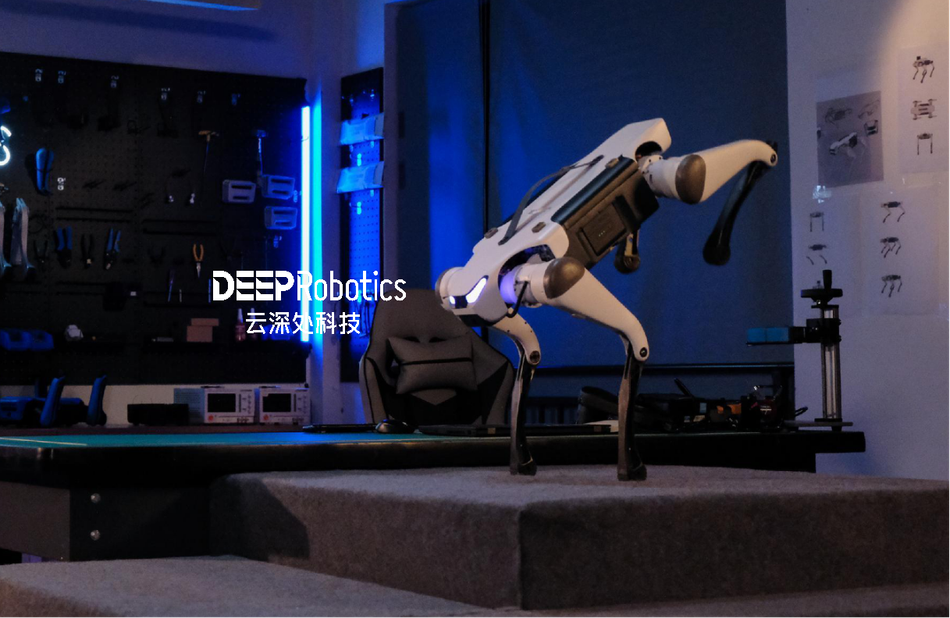

How can quadruped robots help with academic research?
Quadruped robots can be beneficial for academic research. They differ from two-legged, wheeled or tracked robots because they can navigate multiple terrains and perform high-risk tasks without endangering human life. Quadruped robots can be used in various fields, such as locomotion and biomechanics studies, refining robotics algorithms and control systems, artificial intelligence and machine learning, and human-robot interaction. These robots can provide researchers with valuable insights and help advance scientific knowledge across multiple disciplines.
DEEP Robotics’ robot dogs are already used by some universities, including Tsinghua, Peking and Edinburgh, and University College London. The new Lite3 is positioned to be affordable for research purposes as well as for robotics enthusiasts.
Open modular structure
The open modular structure and interfaces of the Lite3 make it highly scalable and flexible in its capabilities. Modules such as ones for Real-Time Kinematic (RTK), artificial intelligence, edge processing and other types of sensors can be readily added.
To enhance its navigation across very challenging terrain, the Lite3 provides levelled–perception capability interfaces (SDK, API) combined with LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) and depth camera to develop auto-navigation, auto-stop, obstacle avoidance, visual positioning, 3D scanning and other perceptional abilities.
To find out more about where you can purchase a Lite3 quadruped robot, visit our website.