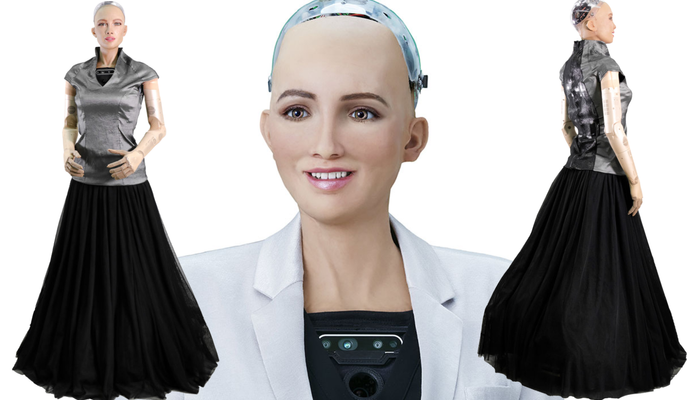
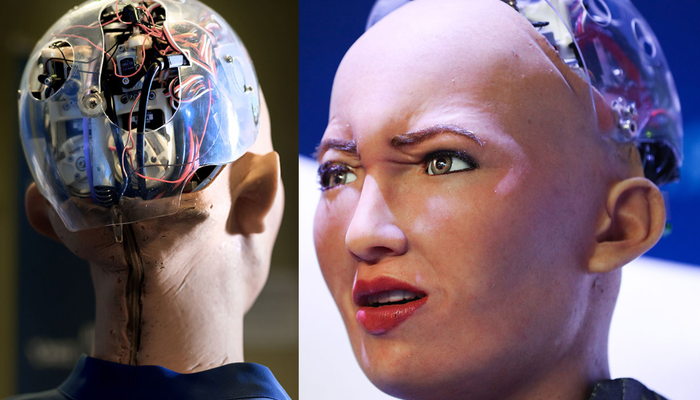
Sophia: A realistic humanoid robot
A humanoid robot capable of human-like expression and human interactions via AI
Technical Specifications
| Height | 167 cm | 65.7 in |
| Width | 41 cm | 16 in |
| Weight | 20 kg | 45 lb |
| Sensors | |
| Camera | Intel RealSense camera |
| Chest: Custom wide-angle 1080p | |
| Eyes: Two custom 720p HD cameras each | |
| Microphone | External USB microphone |
| Arm | Arm joints: joint angle sensors and force sensors |
| Fingers: Touch sensors | |
| Other | Audio localization array; Inertial measurement unit (IMU) |
| Actuators | |
| Head and face | Five Dynamixel XM430 servos and 23 Xpert servos. |
| Eyes | Two Hitec HS-65MG servos |
| Neck | Three Dynamixel XM430 servos |
| Arms and hands | Two Dynamixel MX64 servos, one Dynamixel MX106 servo, four Dynamixel XM430 servos, six Xpert servos, and two MKS servos (per arm/hand) |
| Power | 110/220-V power supply or 24-V lithium-polymer battery |
| Computing | 3 GHz Intel i7 with 32 GB RAM, integrated GPU |
| Software | Ubuntu Linux OS, Ethernet, Wi-Fi |
| Degrees Of Freedom (Dof) | 83 (Head and neck: 36 DoF; Arm and hand: 15 DoF x 2; Torso: 3 DoF; Mobile base: 14 DoF) |
| Materials | Frubber (actuated skin), carbon fiber, CNC aluminum, steel, Spectra fiber, Delrin thermoplastic, acrylic, polycarbonate, 3D-printed parts, and other mixed media. |
Overview
Problem / Solution
Robotics has long been a significant element of the industry, and researchers have recently begun to pay attention to artificial intelligence, which has led to the creation of an AI robot. Robots with artificial intelligence are being developed more frequently today. Robotics are created to make people's lives easier; with AI, robots can navigate independently, decide what to do, and adapt to different conditions. AI robots' industrial, military, medical, exploratory, and entertainment applications are possible. AI robots need methods for navigating different settings, interacting with people, and dealing with circumstances requiring complicated semantics.
Hanson Robotics created Sophia, a humanoid robot that can interact with people, display life-like facial expressions, and express a wide range of sophisticated and sensitive emotions. It includes features for facial recognition, visual tracking, and other AI-based activities, as well as natural language processing and voice. Sophia is intended for use in research, education, and entertainment, and it aids in fostering societal debate on AI ethics and the potential of robotics. It can also be viewed as a framework for cutting-edge robotics and AI research, particularly in human-robot interactions and their potential uses in entertainment and service.
Design
Sophia, regarded as Hanson Robotics' most advanced human-like creation, personifies the potential of artificial intelligence. A platform for cutting-edge robotics and AI research, Sophia combines science, engineering, and the arts to showcase the future of AI and robotics. Sophia demonstrates how each person's conception of an AI robot differs. As a result, Sophia is regarded as the first robot citizen in the world and the first robot Innovation Ambassador for the UNDP.
Appearance
Sophia is created to have a human-sized look with a genuine human-like expressive face, patented artificial skin, and configurable skin tone, facial design, language, and arm colors.
Expression
The artificial intelligence robot has a life-like expressive face that can mimic human emotional expressions. It can also interpret sentences and context with a cloud connection and synchronize its mouth, face, and body when speaking.
Motion
The AI robot has 74 degrees of freedom in its mobility and articulated fingers, arms, and shoulders. Each hand has a payload capacity of 600grams. Including self-navigation, Sophia has three distinct rolling base options.
Sensor
Sophia is incorporated with face detection and body tracking features. These sensors can be programmed for a wide range of physical interaction tasks.
Operating System – Hanson AI SDK
The Hanson AI SDK controls Sophia's AI-based perception, NLP algorithms, open domain chat functionality, non-verbal language, low-level sensory input, and actuation controls.
Artificial Intelligence
Modern research in symbolic AI, neural networks, expert systems, machine perception, conversational natural language processing, adaptive motor control, and cognitive architecture are all combined in Sophia's AI. Since Sophia's AI components can be combined in numerous ways, its reactions may alter depending on the context or other factors.
Modern machine perception makes it possible to distinguish human faces, identify different hand motions, and see emotional expressions. During a conversation, the AI robot may infer emotions and attempt to interact successfully with people. It can simulate human psychology and different brain regions to have its own emotions. Through the application of the Tononi Phi assessment of consciousness, it was shown Sophia might also have a simple type of consciousness based on the data processed and circumstance.
In addition, it uses route planning and IK solver to control its hands, sight, movement, and dynamic stabilization for adaptive walking. Most of the time, it operates in fully independent AI mode, but occasionally, its AI mingles with words created by humans. Engineers, artists, and scientists still control AI robots' conversations, behaviors, and mind. Hence, Sophia can be referred to as having "hybrid human-AI intelligence."
Connecting with humans
It is integrated with a collective intelligence dubbed Sophia Intelligence Collective, a combination of true AI and human input (SIC). This SIC is regarded as trust between people and Sophia, in which the team mentors the AI robot through the ups and downs of its development in the hopes that it will develop actual sentience and become an adult with human-like characteristics.
Sophia can use its real AI to create some of its own thoughts, speech, and actions. Through her contacts with people, Sophia develops and uses this invaluable knowledge to achieve genuine autonomy and sentience.