Cleaning Circuit Boards: A Complete Guide for Engineers and Technical Professionals
Learn the best methods and industry standards for cleaning circuit boards, removing contaminants like dust, flux residues, and corrosion to ensure optimal performance and longevity!
Precision Cleaning Brush on an Electronic Board
Introduction
Cleaning circuit boards is an essential maintenance task in electronics engineering! Even the best-designed printed circuit boards (PCBs) can suffer performance issues or failures if contaminants build up on their surfaces. Dust, flux residue from soldering, and corrosion deposits can all disrupt the delicate electrical pathways on a PCB.
For example, a layer of dust can block airflow and insulate heat, causing components to overheat. Dirt combined with humidity can accelerate corrosion on component leads and PCB traces. Flux residues left after soldering are hygroscopic – they absorb moisture – and can form conductive films that lead to leakage currents or even shorts over time. In short, contamination undermines the performance and longevity of a circuit.
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of cleaning circuit boards, covering industry-standard methods, recommended cleaning agents, and best practices for safe handling. By mastering cleaning circuit boards, engineers can enhance product reliability, improve soldering quality, and ensure compliance with stringent industry standards.
Understanding Circuit Board Contaminants
Before diving into cleaning techniques, it’s important to identify what kinds of contaminants typically plague circuit boards. Different contaminants pose different risks to electronics and may require specific cleaning approaches. The most common PCB contaminants include dust, flux residues, and corrosion/oxidation:
Dust and Particulate Matter
Dust is ever present, and will settle on exposed circuit boards over time! These fine particles can block heatsinks or ventilation paths, causing heat buildup. Dust on a PCB can act like an insulator, preventing proper heat dissipation and leading to overheating of components. In high humidity, dust can absorb moisture and potentially create conductive paths that induce short circuits or accelerate corrosion.
Flux Residues from Soldering
Solder flux is used during assembly to help solder flow and bond by removing oxides from metal surfaces. After soldering, flux chemicals often remain as a residue on the PCB. Depending on the type of flux (rosin, no-clean, or water-soluble), these residues can be mildly sticky, acidic, or ionic.
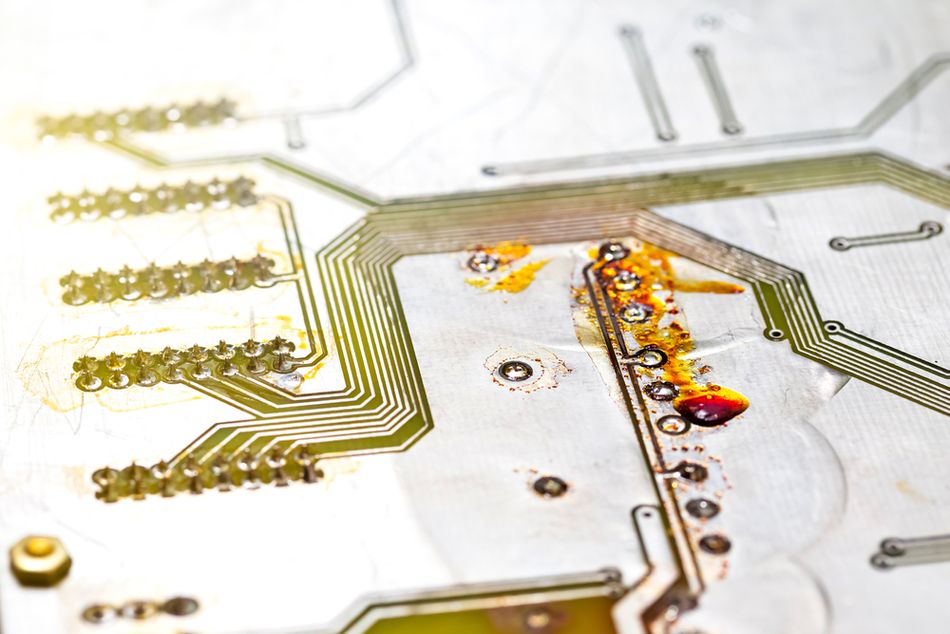

Some flux residues are also slightly conductive or corrosive in the presence of humidity. Even "no-clean" flux, designed to be left on boards, can become problematic in high-voltage or high-humidity environments, compromising long-term reliability. [1] Proper flux removal is essential to prevent performance degradation and component failures.
Corrosion and Oxidation
Corrosion on a circuit board typically appears as tarnish, rust, or a bluish-green crust (especially on copper-containing parts) and is a result of metal reacting with oxygen, moisture, or other corrosive agents. This often happens when PCBs are exposed to water, high humidity, salt spray, or leaking batteries.
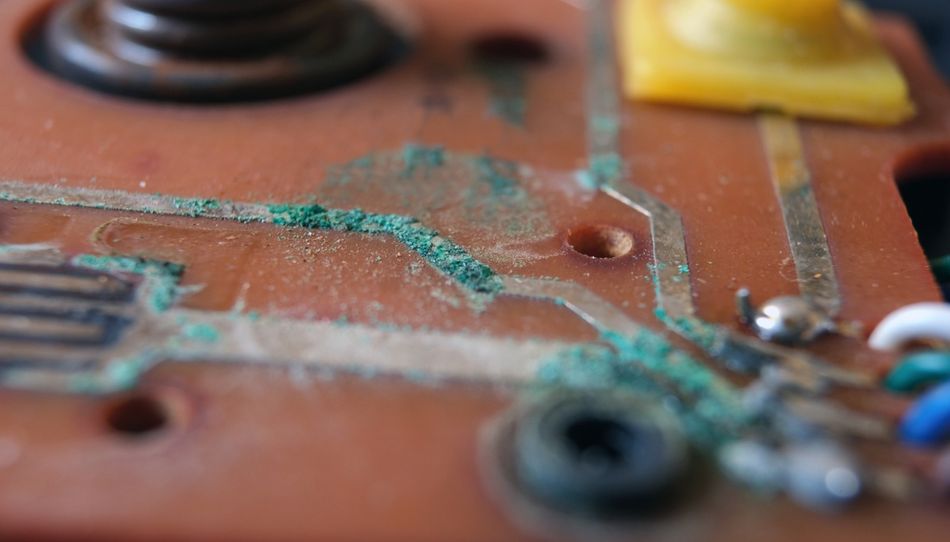

Corrosion and oxidation are especially harmful because they directly attack the materials of the PCB. Unlike dust or flux that sit on the surface, corrosion changes the metal itself. Preventing corrosion through proper cleaning processes and protective measures is crucial for long-term reliability.
Recommended Reading: PCB Manufacturing Process: Everything You Need to Know
Cleaning Methods Based on Contaminant Type
Not all dirt is equal – the optimal method for cleaning a circuit board depends on what you’re trying to remove! Using the right method ensures you clean thoroughly without damaging the board or components:
Removing Dust and Particulates
For loose dust and small debris, dry cleaning methods are typically sufficient! The goal is to dislodge and blow away dust without grinding it into the board or generating static.
Compressed Air Blowing: One of the quickest and most effective ways to remove dust from a PCB is by using compressed air. This method dislodges loose debris from the board and components without requiring direct contact. Hold the can upright and spray short bursts of dry air to blow dust off the board and out from under the components. It’s important to use electronics-grade compressed air and to keep the nozzle a safe distance from the board. Maintain a safe distance from the board to avoid excessive force that could dislodge delicate components or spin cooling fans too fast. Compressed air is simple and effective, but take care not to overspray in one spot, which could freeze the area or create static. When used properly, it safely clears away dust and lint from PCB surfaces and crevices.
Soft Brushing: For dust that’s slightly adhered or caught in corners, gently brushing the board can help. Use a soft-bristle brush (ideally an anti-static PCB cleaning brush) to sweep dust off components and traces. Brushes with conductive or anti-static bristles are recommended to prevent buildup of static electricity while cleaning. Natural fiber or very soft nylon brushes can also work if you’re cautious. Lightly stroke the board to loosen dust, especially in between pins and connectors. Do not scrub aggressively – the idea is to free the dust, not to scratch the PCB solder mask or knock off parts. Often, brushing is done in conjunction with blowing air: brush the dust loose, then blow it away. Hold the board at an angle so dust falls away, or air dry after brushing to ensure removed particles don’t resettle.
Vacuuming (with Caution): Another way to remove dust is by suction! Ideally, electronics-safe vacuums or small battery-powered PCB vacuums can pick up dust without blowing it elsewhere. If using a vacuum, ensure it’s designed for electronics – it should be ESD-safe and low-power. Standard household vacuums are not recommended, as their nozzles can generate static and their strong suction might snag components. In fact, using an ordinary vacuum on PCBs can cause damage to the board or components. If you have a proper electronics vacuum, gently hover the nozzle above the board to pull dust off. Vacuuming can be especially useful for thick dust build-up or when cleaning inside equipment where blowing dust around isn’t desirable. Always hold the board securely, as the suction can pull the board or small parts if you’re not careful.
For routine dust control, a combination of these dry cleaning methods works best. Regular inspections can prevent excessive buildup—if dust is removed early, a quick air blast or brush-off is often enough to keep the board clean.
Cleaning Flux Residues
Flux residue is a common contaminant on soldered boards, and removing flux after soldering is widely considered best practice to ensure long-term reliability.
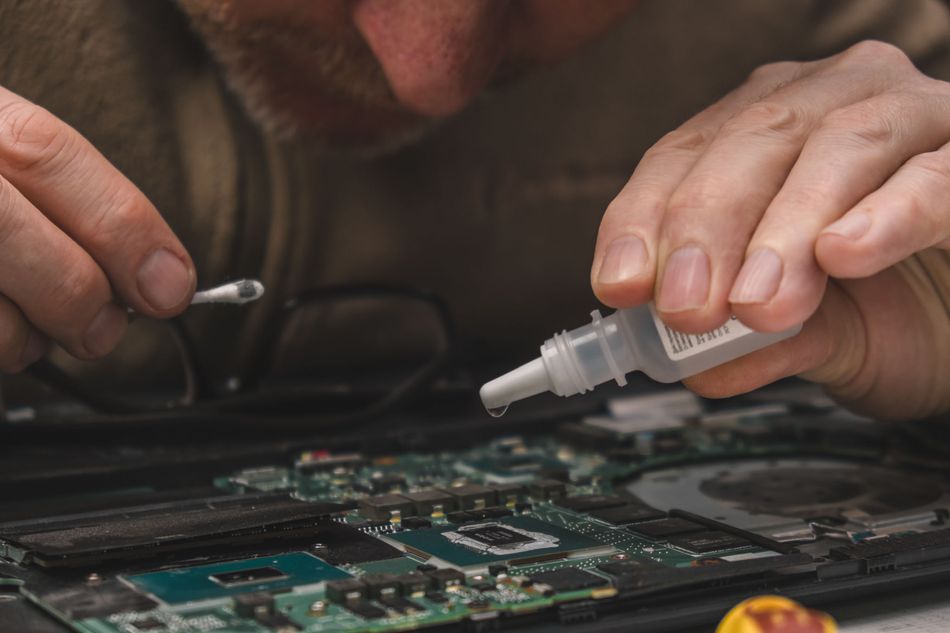

Why Flux Removal Matters? Flux residues (from rosin, no-clean, or water-soluble flux) can lead to corrosion or electrical leakage if left on the board. Even “no-clean” flux, which leaves a minimal supposedly non-conductive residue, can cause problems under certain conditions (like high humidity or high voltage). Moreover, flux residues can trap heat and dirt, and make visual inspection or rework difficult. For high-performance or high-reliability circuits, it’s generally recommended to clean off all flux residues after soldering to avoid any risk of degradation. Many industry standards (e.g., IPC guidelines) set limits on allowable residue on a PCB, underscoring that cleaning is necessary unless you are certain the residue is truly benign.
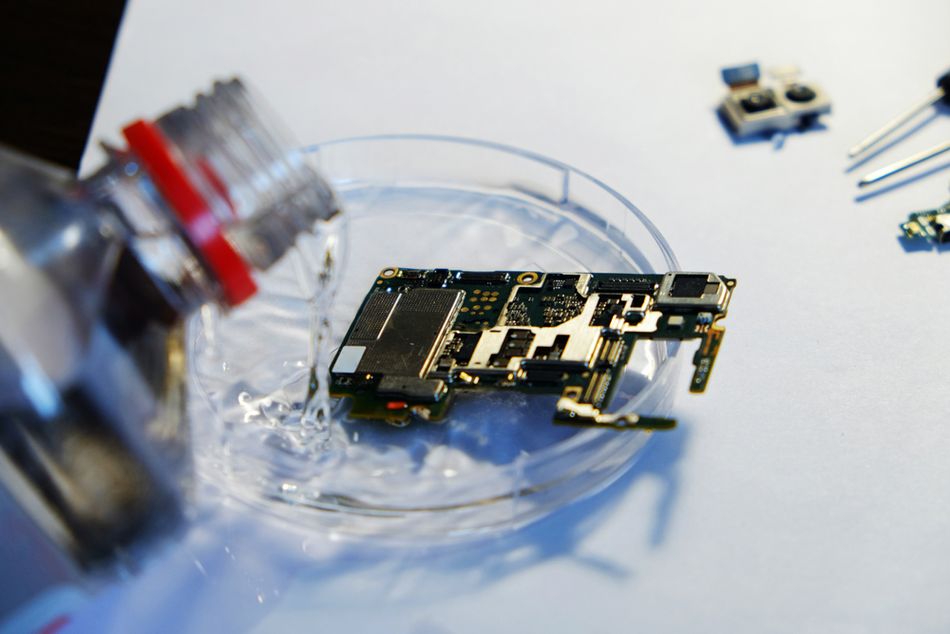
Solvent-Based Flux Cleaning: The most common method to remove flux is using solvents. Isopropyl Alcohol (IPA) is a go-to solvent for engineers and technicians. High-purity IPA (90% or above) effectively dissolves rosin and many no-clean flux residues, as well as oils and grime, and it evaporates without leaving residue. [2] To clean with IPA, apply it to a cotton swab, lint-free wipe, or soft brush and gently scrub the fluxed areas. The alcohol will dissolve the flux, which you can then wipe away. It helps to use a flux cleaning brush dipped in IPA to lightly scrub solder joints and between pins. The dissolved flux can be blotted with a wipe. In professional settings, commercial flux remover solvents are also popular – these come in spray cans or bottles and are specifically formulated to break down flux. They often contain alcohols or other solvents and sometimes dry even faster than pure IPA. The end result should be a clean PCB with no sticky, white, or discolored residues.
Water-Based (Aqueous) Flux Cleaning: Water-soluble flux (organic acid flux) is designed to be removed with water, making aqueous cleaning an effective option in manufacturing environments. It is crucial to use deionized (or distilled) water rather than tap water – deionized water has no ions/minerals, so it will not leave conductive mineral deposits or cause immediate corrosion. Gently scrub the board with a soft toothbrush or anti-static brush to remove residue from tight spaces. Rinse thoroughly to ensure no moisture or residue remains, as even small amounts of ionic contamination can lead to corrosion over time. Water cleaning is only suitable for water-soluble fluxes. Attempting to clean rosin or no-clean flux with water can leave behind white residues and fail to remove the flux effectively. If your flux is not specifically water-washable, stick to solvent-based cleaning.
Stubborn Flux and Combination Methods: Sometimes flux residues (especially old, baked-on rosin) can be stubborn. In such cases, a combination of methods helps. You might spray flux remover to saturate the residue, use a brush to agitate it, and then rinse with IPA or water. Some specialized saponifier solutions (alkaline cleaners) are available which, when mixed with water, help dissolve rosin flux much better than water alone. These are used in industrial PCB washers. Ultrasonic cleaning with the right solution can also remove flux under tightly spaced components. The key is to ensure all residue is dissolved and washed away because any flux left under ICs or connectors can cause reliability issues down the road. Inspect the board under good light after cleaning; if you see any whitish residue or tacky areas, repeat the cleaning until the board is truly clean.
In summary, always consider the flux type: remove rosin and no-clean flux with IPA or specialized solvents, and remove water-soluble flux with water (DI) – but in all cases, get that residue off the board. It’s an important step to prevent corrosion and unintended electrical leakage on your circuits.
Addressing Corrosion and Oxidation
Dealing with corrosion on a circuit board is more challenging – by the time you see corrosion, some damage is already done. However, proper cleaning can stop further deterioration and sometimes restore functionality if the corrosion isn’t too severe.
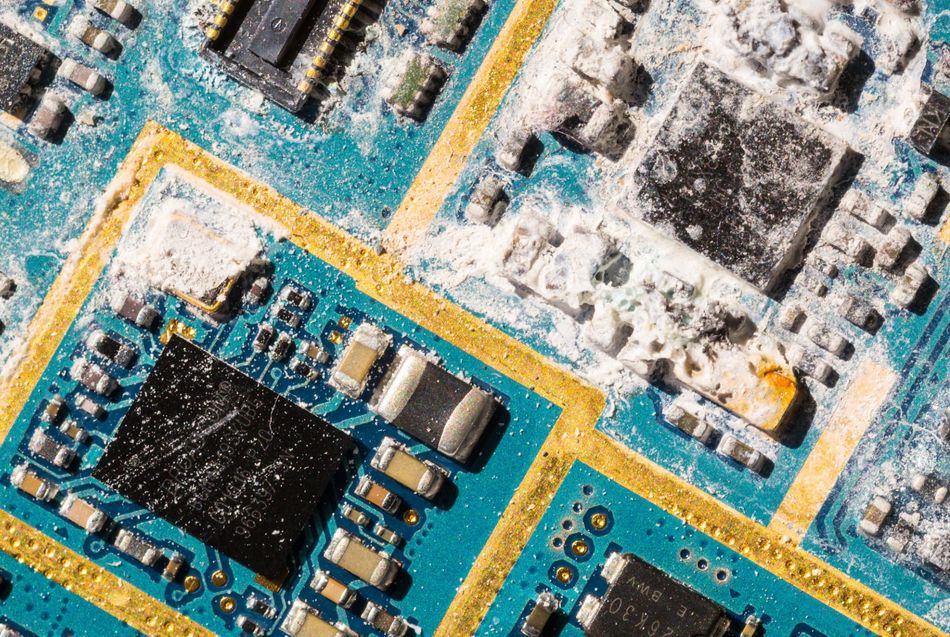
Identify the Corrosion Type: First, determine what kind of corrosion you have! Common scenarios include battery leakage (alkaline or acidic residue corroding the PCB near battery contacts), environmental oxidation (uniform tarnish or verdigris on copper due to humidity and air exposure), or liquid damage (spilled drinks or water causing rust and corrosion in patches). Green or bluish crystalline deposits usually indicate copper oxide/carbonate (often from alkaline exposure), while white powdery residue could be dried acid or salts. Rusty brown areas might mean iron or steel parts (screw heads, component leads) have rusted. Knowing the cause helps choose a cleaning method – e.g., alkaline battery leaks are neutralized by acids (like vinegar), whereas acid spills are neutralized by bases (like baking soda).
Initial Dry Brushing: If the corrosion is dry and flaking, start by carefully brushing away loose debris. Use a soft toothbrush or ESD safe brush to gently remove crusty deposits. Make sure to do this over a workspace where falling debris won’t damage other things. This mechanical removal gets rid of the bulk of the corrosion products. Be gentle – corroded areas might have weakened board material or components. Brushing helps expose the affected areas so chemical cleaners can penetrate better in the next step.
Chemical Cleaning and Neutralization: To effectively remove corrosion, a chemical approach is often required to neutralize and dissolve the affected areas. For alkaline battery leakage, white vinegar (acetic acid) is a proven solution. Alkaline corrosion, typically from potassium hydroxide, forms a carbonate crust that vinegar helps break down. Apply vinegar with a cotton swab or brush, allowing it to fizz as it reacts. Let it sit for a couple of minutes before scrubbing gently to lift the deposits. After treatment, rinse thoroughly with distilled water to remove acidic residues, followed by an isopropyl alcohol (IPA) rinse to eliminate moisture and prevent future oxidation. For acidic corrosion, such as from Ni-Cd battery leaks, the opposite approach applies. Use a baking soda paste to neutralize acidic residues. Apply the paste to corroded areas, let it react, and then scrub gently. Afterward, rinse thoroughly with distilled water and follow up with an IPA rinse for complete removal. Always ensure fast drying to prevent lingering moisture, which could accelerate corrosion.
Solvent and Ultrasonic Cleaning: Once corrosion and oxide have been chemically treated, it’s useful to go over the area with a solvent like IPA or an electronic contact cleaner. This helps remove any remaining moisture and will wash away tiny loosened particles. In cases of widespread corrosion, an ultrasonic cleaner with an appropriate solution can be very effective. An ultrasonic cleaning bath can shake loose corrosion from under component leads and in crevices. However, be cautious: not all components handle ultrasonic vibrations well, and you must dry the board completely afterwards. For localized corrosion, manual cleaning is usually sufficient. After cleaning and rinsing, pat the board dry with lint-free wipes and/or blow it dry with compressed air. If possible, let it dry in a warm environment (or low-temperature oven at ~50°C) for an hour or more to ensure all moisture evaporates.
Assess Damage and Repair if Necessary: Cleaning removes the corrosion, but it might reveal damage left behind. Inspect the once-corroded areas for signs of pitted or eaten-away copper. You may find that some solder pads or traces are partially gone. If so, those might need repair. Also, check component leads that were corroded – are they significantly thinned or cracked? If a component leg is nearly dissolved, that part might need replacement. In many cases, if corrosion is caught early, cleaning will restore the board’s normal operation. If corrosion was advanced, you may have to do a bit of rework to fix the damage it caused.
Corrosion Inhibitors/Protection: After the board is clean and dry, it can be wise to protect the previously corroded area to prevent recurrence. Some technicians apply a thin coat of corrosion inhibitor spray or a fresh layer of conformal coating on the repaired area. For instance, a product meant for PCB protection can deposit a thin film that resists moisture. This is more common in industrial maintenance. At a minimum, ensure the enclosure of electronic device (if any) is sealed or the board is kept in a less harsh environment going forward.
Cleaning corrosion is arguably the most painstaking PCB cleaning task – it often involves multiple steps (neutralize, scrub, rinse, dry) and careful inspection! However, it is critical to stop the corrosion process.
Recommended Reading: ESD Safe Materials: A Beginner's Guide
Recommended Cleaning Solutions and Tools
Now that we’ve covered how to clean various contaminants, let’s look at what to clean them with! Using the right cleaning agents and tools will make the job easier and avoid unintended damage. In professional electronics manufacturing and repair, there are well-established materials for PCB cleaning.
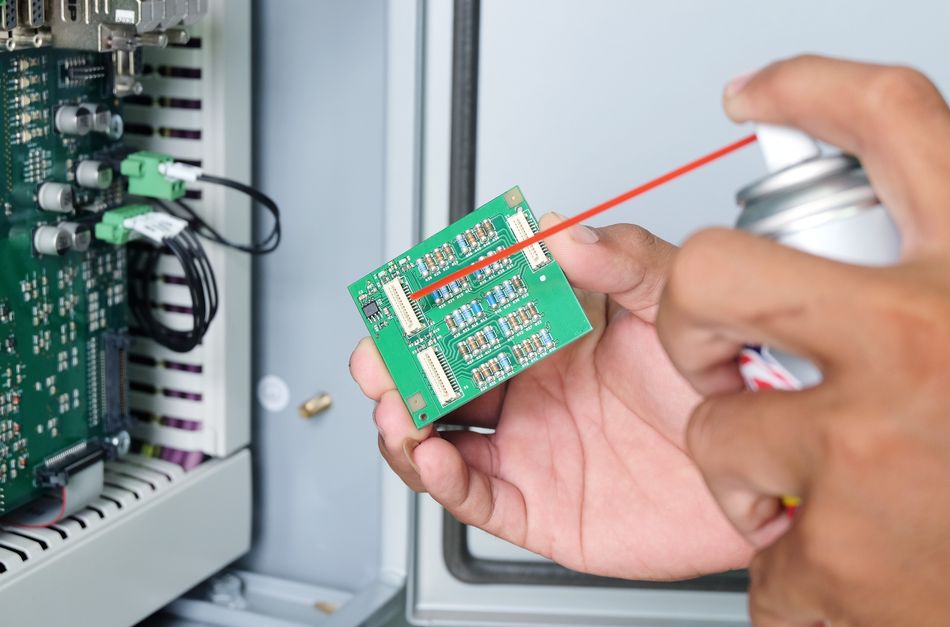
Common Cleaning Agents (Solvents and Solutions)
Isopropyl Alcohol (IPA): High-purity isopropyl alcohol is a staple for PCB cleaning! It’s effective at dissolving a wide range of residues – from flux and oils to light grime – and it evaporates quickly without leaving residue. IPA is relatively safe for most PCB materials and is inexpensive. Typically, 90% or higher concentration IPA is recommended for electronics (70% rubbing alcohol has too much water, which can be less effective and slow to dry). IPA is the “all-purpose” cleaner used both in industry and hobby electronics: you can soak boards in it, use it with swabs/brushes, or put it in an ultrasonic cleaner. Allow the alcohol to fully evaporate before powering up the board, and use it in a well-ventilated area. The popularity of IPA stems from its balance of cleaning strength and gentleness – it can handle sticky flux yet won’t typically harm components or PCB coatings.
Deionized Water: Deionized (DI) water is used mainly for rinsing and cleaning water-soluble contaminants. As mentioned, water by itself is used when cleaning boards that have water-soluble flux or after certain chemical cleanings. The key is that the water must be purified (deionized or distilled) so that it does not contain ions that can deposit on the board and cause conductive residue. DI water is extremely pure and actually a poor conductor, making it safe to rinse electronics when power is removed. It’s often heated and sprayed in PCB cleaning machines to wash off flux and soldering residues. While water is great for removing ionic contaminants and soluble dirt, it won’t dissolve rosin or oily substances. So it’s usually used in combination with detergents or just as a final rinse.
Specialized PCB Cleaners: There are many commercial cleaning products formulated for electronics. Flux remover sprays are one example – these are solvents (or solvent blends) in aerosol form that quickly break down flux. [3] They are convenient for post-soldering cleanup; you spray on the board and often see flux residue dissolve and drip off. Some are no-rinse (evaporative), while others may need a wipe-down. Similarly, electronic contact cleaners are sprays meant to clean contacts and components. They typically are fast-drying solvents that leave no residue and remove oxidation, oil, and dirt. Contact cleaners are safe on plastics and PCBs and can be used to flush out potentiometers, edge connectors, switches, and so on. These specialized cleaners are great for targeted tasks – for instance, removing oxidization on a slot connector or cleaning a dirty PCB edge connector.
Ultrasonic Cleaning Solutions: If you use an ultrasonic cleaner for PCBs, you’ll need a proper solution in the tank. Usually, this is mostly distilled water with a small amount of a solvent or surfactant. Many manufacturers sell ultrasonic cleaning concentrates specifically for electronics, designed to remove flux and residues when agitated with ultrasound. Often these are mild saponifiers that can clean both ionic and non-ionic contaminants. A common DIY solution is distilled water with a few drops of dish soap or a bit of isopropyl alcohol – this can work for light cleaning. The ultrasonic action will create tiny cavitation bubbles that help lift grime without harsh scrubbing. The ultrasonic cleaning should be followed by a thorough rinse in DI water (if the solution leaves residue) and drying. It is important to note that, not all components can be ultrasonically cleaned (e.g., avoid ultrasonic for certain MEMS sensors, mic microphones, quartz crystals, etc., as it can damage them).
Other Solvents: There are a few other solvents occasionally used in PCB cleaning, though with caution. Acetone is a powerful solvent that will strip flux quickly, but it’s very harsh – it can dissolve many plastics, remove conformal coatings, and even attack some PCB materials if used improperly. Generally, acetone is not recommended unless you have a specific reason and know what you’re doing. Denatured alcohol is sometimes used similarly to IPA, but it usually contains contaminants that can leave residues, so it’s less ideal. Chemical oxidizers like hydrogen peroxide are not typical for cleaning electronic boards. In some corrosion cases, a mix of vinegar (acid) and a little peroxide is used to etch away corrosion, but one must be careful not to also etch good copper. Baking soda paste can polish contacts a bit while neutralizing acid – this can be useful on battery terminals. Overall, sticking to the known electronics cleaners is safest.
Essential Tools for PCB Cleaning
Having the right tool for the job can make PCB cleaning much more effective and safe.
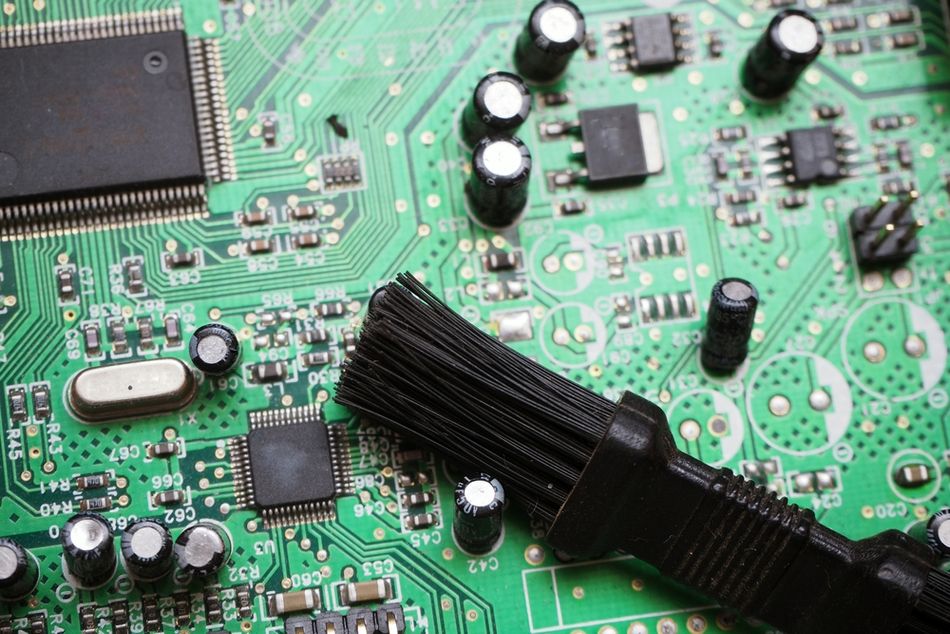
Anti-static Brushes: We’ve mentioned brushes for dusting and scrubbing – it’s worth reiterating that using ESD-safe brushes is important. These are brushes with conductive bristles that prevent static buildup and safely discharge static to the ground. They come in various sizes: a large one to sweep a whole board, and tiny brushes to get between IC pins. Keep a set of these for different purposes – one might be reserved for scrubbing flux with solvent, and another is kept clean for dust only. If you don’t have an official PCB brush, a brand new toothbrush can work in a pinch for scrubbing flux or corrosion – just be aware it’s not anti-static, so only use it on unpowered boards and ideally wear a wrist strap while doing so.
Cotton Swabs and Foam Swabs: Swabs are excellent for precision cleaning. Standard cotton swabs (Q-tips) are cheap and effective for applying solvents and wiping small areas, though they can leave tiny fibers. There are also lint-free foam swabs or polyester swabs made for electronics cleaning which don’t leave fibers. Swabs are especially useful for removing flux around IC pins, cleaning corners, or dabbing small amounts of solvent onto a spot. For example, you can dip a swab in IPA and scrub between fine-pitch pins to clear flux. They’re also great for applying a bit of vinegar exactly where you need it on a corroded joint. Always have a bunch of swabs on hand; use one and discard it as soon as it’s dirty to avoid smearing dissolved gunk back onto the board.
Lint-Free Wipes: When wiping down a PCB, use lint-free cloths or wipes (e.g., Kimwipes or microfiber cloths). Regular tissues or paper towels tend to shred and leave paper fibers on the board, which defeats the purpose of cleaning. Lint-free wipes ensure you don’t add new debris. They are useful for the final wipe after dissolving flux or to blot up dirty solvents. Some technicians also use PEC Pads (lint-free photographic wipes) for delicate cleaning. If a wipe gets soaked with flux or dirt, switch to a clean one rather than smearing contaminants around.
Tweezers and Picks: Sometimes you’ll encounter a sticky blob of dirt or a piece of debris lodged somewhere that requires mechanical removal. ESD-safe tweezers can be used to pluck out things like pieces of lint, solder blobs, or insect debris. Plastic or wooden toothpicks can help scrape off tough flux residues or corrosion spots gently without scratching the board (wood and some plastics are softer than the PCB mask). These tools assist in targeted cleaning tasks but use them carefully to avoid gouging the PCB or slicing a solder mask.
Ultrasonic Cleaner: An ultrasonic cleaning machine is a device that can greatly simplify cleaning for multiple or very dirty boards. Ultrasonic cleaners range from small hobby units to large industrial tanks. For PCBs, you would fill it with a mix of deionized water and a bit of electronics cleaning solution. Place the board in the basket and run the cleaner for a few minutes. The ultrasound will reach under ICs and into via holes, etc., removing contaminants that brushing might miss. Afterward, rinse the board and dry it. While ultrasonic cleaning is generally safe for many electronic assemblies and provides, a very thoroughly clean, certain sensitive components might be damaged by it. If in doubt, consult component datasheets or skip ultrasonic for those parts.
Automated Cleaning Systems: In production environments or for high-volume operations, there are automated PCB cleaning machines. These include spray-in-air cleaners, where boards pass through a chamber and are blasted with cleaning solution and water rinse, or batch cleaning systems that wash multiple boards at once. There are also vapor degreasers, which clean using solvent vapors. While such equipment is beyond the scope of what an individual engineer would use on a bench, be aware that these exist. They are used to meet strict cleanliness requirements in industries like aerospace. If you work with assembly houses, they might clean your boards using such machines. The principle is the same: apply the appropriate solvent or aqueous solution, physically dislodge residues, then rinse and dry.
ESD Precautions Gear: While not a cleaning tool per se, it’s worth mentioning that you should use an anti-static wrist strap or ESD mat whenever handling PCBs outside of their equipment, especially when doing extensive cleaning or rework. Cleaning often involves rubbing and moving brushes, which can generate static. To protect sensitive electronic components from electrostatic discharge, always ground yourself and ideally do the cleaning on an anti-static mat. Also, wearing nitrile gloves not only protects your skin from chemicals but also keeps fingerprints off the board. Many cleaning solvents are flammable, so keep away from open flames or sparks, and ensure the area is ventilated.
By assembling a PCB cleaning kit with the solvents and tools above, you’ll be prepared to tackle just about any dirty board you come across. Having these dedicated tools also prevents you from improvising (like using a shirt sleeve or kitchen sponge – not good ideas on electronics).
Recommended Reading: PCB Testing: A Comprehensive Guide to Techniques, Tools, and Best Practices
Best Practices for Safe and Effective PCB Cleaning
When cleaning circuit boards, technique matters as much as tools and solvents. It’s easy to accidentally cause damage if you’re not careful – for example, by applying too much force or not fully drying a board.
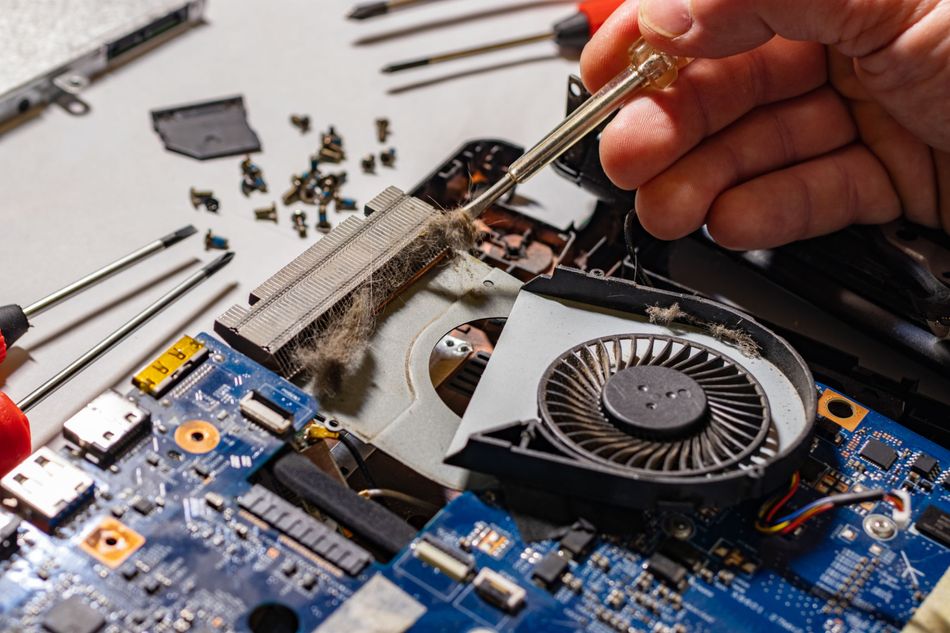

Power Down and Remove Power Sources: Always ensure the circuit is completely powered off and disconnected before cleaning. This means unplugging the device and also removing any batteries. Attempting to clean a live board is dangerous and can short the circuitry or shock you. Additionally, discharge any large capacitors if present (following proper safety for high-voltage sections) before handling.
ESD Protection: Handle the board in an electrostatic discharge safe manner. Wear a grounded anti-static wrist strap and/or work on an ESD mat to avoid zapping any sensitive ICs with static. Many cleaning actions (like brushing or wiping) can generate static, so it’s important to be grounded. Also try to use ESD-safe tools to further reduce static risk. Remember, you won’t necessarily feel a static shock that can still destroy a microchip, so take precautions even if the board seems “dead.” ESD damage is invisible and irreversible!
Work in a Well-Ventilated Area: Many cleaning solvents (IPA, acetone, spray cleaners) have fumes that you should not inhale in high concentrations. [4] Always use these chemicals in a ventilated space – for instance, near an extractor fan or open window – to avoid breathing vapors. If you’re using aerosol cleaners, short bursts directed at the board and then stepping away is wise. Good ventilation also helps flammable vapors dissipate to reduce fire risk. In professional settings, a fume hood or extractor is used when cleaning with solvents. At a minimum, ensure you’re not in a tiny closed room building up solvent fumes.
Wear Appropriate PPE: Protect yourself by wearing gloves (nitrile or latex) when handling cleaning agents, especially stronger chemicals, or if you’ll have prolonged contact. Solvents can defeat your skin or cause irritation. Gloves also keep fingerprints and skin oils off the board – two birds with one stone. Safety glasses are recommended if using any sprays or if there’s a risk of debris flying. The last thing you want is a speck of flux or a drop of alcohol in your eye. In summary, gloves, eye protection, and even a lab coat or apron are good to use for larger cleaning tasks.
Be Gentle with Components: When scrubbing or handling the PCB, use only the necessary amount of force. Small SMD parts or wire connectors can break off if you scrub aggressively. If a deposit is not coming off easily, rather than forcing it mechanically, try a longer chemical soak or a different solvent. Improper cleaning can do more harm than good – for instance, a rushed, aggressive cleaning might knock a vital resistor off the board or scratch through a trace. So take your time and treat everything delicately.
Thorough Drying is Crucial: After any wet cleaning (water, alcohol, etc.), make sure the board is completely dry before reassembly or power-up. Use compressed air to blow out water from underneath ICs or connectors. You can also pat the board with lint-free wipes to absorb the bulk of the moisture. Heating speeds up evaporation and ensures that even moisture trapped in tiny gaps comes out. If you use water to wash, this step is especially important – water can hide under BGA chips or inside potentiometers. Do not rush to power the board on until you are confident it’s dry. Proper drying process prevents residual moisture from causing short circuits or corrosion later.
Inspect After Cleaning: Once you think the board is clean and dry, do a careful inspection under good light. Look for any remaining residue: white patches (could indicate dried flux or cleaner residue), greenish tinge (leftover corrosion), or any fibers/hairs. If you see something, clean that spot again. Ensure no unintended materials are left: for example, occasionally a bristle from a brush might come off and stick to the board – remove it. If the board has connectors or sockets, inspect that no moisture is pooled inside them. This inspection is your chance to verify the cleaning was successful before powering up.
Handle Clean Boards with Care: Handle the cleaned PCB by the edges or wear gloves to avoid re-depositing oils. If you need to store the board or ship it, put it in a clean anti-static bag or a clean enclosure. For long-term storage, consider anti-tarnish bags or even adding silica gel desiccant in the package to absorb moisture. The idea is to keep it clean and dry so you don’t have to repeat the process. The prevention of contamination is easier than constant cleaning: for example, using conformal coating on a board can protect it from dust and moisture if the device is in a harsh environment, reducing how often you’ll need to clean it.
Follow Manufacturer Guidelines: If you have access to manufacturer documentation for either the PCB assembly or certain components, heed any cleaning guidelines they provide. Some sensitive components may be labelled as “do not clean” or might require specific methods (for instance, some sensors have stickers you shouldn’t remove except if you plan to wash the board, etc.). Additionally, organizations like IPC have standards on acceptable cleanliness and methods – if you’re cleaning boards professionally, familiarize yourself with those.
By following these best practices, you’ll ensure safe, effective, and damage-free PCB cleaning. Prioritize safety and precision—a clean board is valuable, but not at the cost of damaging components!
Recommended Reading: How Do Circuit Boards Work: A Comprehensive Guide to the Heart of Electronics
Conclusion
Keeping circuit boards clean is essential for reliability and longevity in electronics. This guide covered dust, flux, and corrosion removal, along with the best cleaning methods—compressed air, solvents, and chemical neutralization. Using the right tools like IPA, deionized water, brushes, and ultrasonic cleaners ensures safe and effective cleaning. Proper drying and ESD precautions prevent damage, making PCB maintenance a key part of preventative care. Whether in hobby projects or industrial equipment, clean PCBs reduce failures and improve performance. With the right techniques and materials, engineers can maintain electronics at peak efficiency, ensuring lasting operation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: How often should PCBs be cleaned?
A: Cleaning frequency depends on the environment! Indoor boards may only need occasional cleaning, while industrial or dusty environments require maintenance every 3–6 months. Mission-critical systems should be inspected and cleaned more frequently. Monitor for dust, flux, or corrosion, and clean proactively to prevent failures.
Q: What is the safest solvent for cleaning circuit boards?
A: High purity isopropyl alcohol (IPA, 90% or above) is the safest and most effective solvent. It evaporates quickly, leaves no residue, and removes flux, oils, and dust. Electronics-safe contact cleaners are also reliable. Avoid acetone and strong solvents, which can damage plastic components and coatings.
Q: Can I use water to clean a PCB?
A: Yes, but only deionized (DI) or distilled water to prevent mineral deposits. Rinse thoroughly and fully dry before powering up. Water-soluble fluxes clean well with DI water, but rosin flux requires IPA. Avoid tap water, as residual minerals can cause corrosion or conductive buildup.
Q: What’s the best method to remove corrosion from a circuit board?
A: Neutralize and dissolve corrosion based on its type. Use white vinegar for alkaline battery leaks or baking soda paste for acidic corrosion. Scrub gently, rinse with distilled water and follow up with an IPA rinse. Fully dry the board to prevent further damage.
Q: Do ultrasonic cleaners damage circuit boards?
A: Ultrasonic cleaning is safe for most PCBs but can damage MEMS sensors, relays, and delicate components. Use a 40 kHz ultrasonic bath with distilled water and mild detergent. Avoid prolonged exposure, and fully dry the board to prevent moisture retention under components.
Q: Is it necessary to remove flux after soldering?
A: Yes, removing flux prevents corrosion, leakage currents, and contamination. Even no-clean flux can cause issues in high-humidity or high-voltage environments. Use IPA or a flux remover for best results. Clean boards are easier to inspect, rework, and ensure long-term reliability.
Q: What precautions should be taken when using cleaning solvents on PCBs?
A: Ensure proper ventilation, avoid open flames, and use nitrile gloves for protection. Power down boards before cleaning. Use ESD-safe tools, apply solvents sparingly, and thoroughly dry the board. Avoid acetone on plastics, and store solvents safely to prevent evaporation or fire hazards.
References
[1] ResearchGate. Decomposition of no-clean Solder Flux Systems and their Effects on the Corrosion Reliability of Electronics [Cited 2025 March 18] Available at: Link
[2] PAC. Why Is 70% Isopropyl Alcohol (IPA) a Better Disinfectant than 99% Isopropanol, and What Is IPA Used For? [Cited 2025 March 18] Available at: Link
[3] Gesrepair. How to Clean a Circuit Board [Cited 2025 March 18] Available at: Link
[4] Microcare. 4 Types of PCB Contamination and How to Remove Them [Cited 2025 March 18] Available at: Link
Table of Contents
IntroductionUnderstanding Circuit Board ContaminantsDust and Particulate MatterFlux Residues from SolderingCorrosion and Oxidation Cleaning Methods Based on Contaminant TypeRemoving Dust and ParticulatesCleaning Flux ResiduesAddressing Corrosion and OxidationRecommended Cleaning Solutions and ToolsCommon Cleaning Agents (Solvents and Solutions)Essential Tools for PCB CleaningBest Practices for Safe and Effective PCB CleaningConclusionFrequently Asked Questions (FAQs)References